How to make a backup of the Android system. How to make a backup copy on Android and make a backup from it
Backup Android- This is a function for creating a backup copy for a gadget, so that in the event of a device or system failure, lost data can be restored. The value of information on smartphones (achievements in games, photos, contacts, messages and correspondence) has led to the growing popularity of the issue.

A full backup of Android means saving all information from the device. It is recommended to use another drive to store data in order to recover lost data in an unexpected situation. Backup involves placing data in a special format, which is not always suitable for reading by programs. In most cases, all the information is embedded in a separate file (like an archive or image), and then you can expand it.
A backup is useful because it allows you to transfer all information to another device. It is also worth creating a backup before performing actions that could damage the system - installing various themes, kernels, programs, etc.
In total, there are 3 main ways to create a backup: system (using functions built into the device), software (through special applications) and cloud (through cloud storage).
How to make a backup on Android without additional programs?
A backup of the Android firmware can be done in Recovery mode, which is built into all smartphones and tablets on the mobile platform. This tool is quite enough to fully save data from all kinds of failures.
The execution method consists of the following steps:
- It is necessary to ensure that the device is sufficiently charged; the function will not start if the charge is less than 50% due to the risk of power loss during the backup process. You must have at least 0.5 GB of free space on your memory card.
- While holding the lock button, you need to completely turn off the device.
- You should hold down the volume up button and the device activation key at the same time.
- After 10-30 seconds, the smartphone will be launched in service mode, and commands to be executed will be displayed on the screen.
- If a broken robot icon appears on the screen with an exclamation mark next to it, you should press the activation key and the volume down.

- Using the volume controls, you need to go to the section called “backup...”.

- To confirm your selection, briefly press the lock key.
- Next, you should go to the “backup” item from the current section; sometimes you have to open another directory before that.
- All you have to do is wait for the process to complete, which takes about 10 minutes. A corresponding window will indicate completion.
- You need to restart the application by selecting “reboot...”.
A backup recovery copy has now been created on the system. The manipulation will not affect the operation of the device in any way. It is recommended to transfer the backup to a computer or flash drive to save the data. You can find the corresponding files in the ClockworkMod directory.

How to make a backup of Android firmware through programs?
Today, many applications have been developed that allow you to create backups on Android. The most common programs:
- Titanium Backup;
- FlashTools SP.
For most users, the utilities listed will be sufficient, although the choice often has to be made based on the firmware and model of the smartphone. Titanium is a fairly universal application; it can be used in 80% of all smartphones.
With Titanium Backup, execution occurs in several stages:
- Launch the application and provide it with .
- Click on the button above, located in the right corner.
- Select “Make r. k. all software".

There is a slightly different principle for creating a backup, which is to use a PC. For this case, it is necessary to enable developer mode and activate USB debugging mode. This is also a software method, so you will need MyPhoneExplorer.
- Activate the application.
- Synchronize gadgets and PC with each other using a USB cable.
- Going to the program, you need to select “File” and the “Connect” item.
- You should expect the smartphone to be detected within 1 minute.
- After the phone appears, you should go to the “Miscellaneous” section and select the option to create a backup.

- Next, you should specify the path to save the data.
- By checking the boxes, you can select all the necessary information on the device.
- After preparation, all you have to do is click on “Create a copy”.

Cloud method
Almost every Android device has a built-in cloud and a Google account. This function is standard and does not depend on the type of firmware and shell. You must create a profile if it does not exist or log in to your own. To perform synchronization, you will need access to the network and sufficient space on the cloud.

To perform a backup, just go to Settings and select the backup item in the personal data category. Here it is worth checking that there are checkboxes next to each entry, at least the most important ones, and then tapping on “Add”.
The listed methods allow you to prevent data loss in any unfavorable cases. If necessary, the created backup can be deployed to another smartphone.
If you still have questions on the topic “What is backup on Android? How to make a backup of Android?”, then you can ask them in the comments
if(function_exists("the_ratings")) ( the_ratings(); ) ?>
In our computer age, it is impossible not to understand what backup is on Android. When working with computer systems and large volumes of material, one inevitably has to think about their safety. Otherwise, something irreparable may happen, and the user will find himself, like the famous old woman, with nothing.
In order not to lose data, you need to constantly backup Android to your computer; no other reliable way to save information has yet been found. There are good instructions for users running the latest versions of computer software on how to set up backups so that in the event of a computer program failure or hardware failure, they remain with the information received. With their help, you can guarantee yourself protection from annoying failures of mobile media.
What is a backup?
Creating a general or partial backup of certain Android data - backup. In particular, this could be a computer program or various user documents. Such a replenishable archive makes it possible to restore information after various program failures or media failure. In addition, backup capabilities allow you to automate the process of transferring existing settings and programs from one device to another. This solves the problem without the need for manual configuration; you can have two operating systems with the same set of existing computer programs and received data.
Backup on Android
What is backup on Android? Today there are a large number of different storage media operating on these computer principles. They can fail at any time, and then the user will need the information. Using the backup procedure, you can restore your operating system relatively easily.

Depending on the form of the backup, it is possible to make a general save of the system, including even the settings of various computer applications, as well as a backup of a specific amount of information from private sectors, for example, important SMS messages for you, necessary electronic contacts, interesting applications, cool photos, etc. .d.
Why make a backup?
So why do you need it and what is backup on Android? Of course, careful activity on the Internet guarantees the normal development of the situation. As can be seen from practice, much more often users who like to take risks with their Android devices are faced with the need to recreate the operating system and data from a backup. As you know, for computer devices there are often a large number of different programs and their elements. When a user regularly changes something in his own device, after some time his device simply breaks down. Moreover, to make a fatal mistake, you don’t need to do anything out of the ordinary; just pressing the wrong button is enough.
However, an ordinary user who does not want to conduct risky experiments with his media may run into other serious problems: malicious viruses, numerous hackers, errors in the program - and there is a need to restore the original form. And for this you need a backup.
Backup principles
How to make a backup on Android? When working with copying information from mobile media, for security and increased efficiency, you must strictly adhere to several simple principles:
- Systematic actions in the process. Creating backups from mobile media should be as mandatory as eating three full meals a day.
- The concept of verification as a mandatory element of backups. It is necessary to examine the backup copy of the data, because for a number of specific reasons the recovery process may be interrupted. It will be quite a shame if, at a particularly dramatic moment, the backup option is a dud. Therefore, after completing the process of creating a backup copy, open random (or the most important) files from the created archive and in practice make sure that they are safe.
- The principle of separation. The best option is to place backups not in one place, but in several, if possible. In particular, on a flash drive, a removable hard drive, in the cloud, etc. After all, hard drives in some cases lose their performance, and the Internet may not be available at the right time.
- Distributing the contents of the backup copy into a number of sections. As you wish, divide the material by importance, topic, volume, etc. Most importantly, you should always know where the necessary material is located, how guaranteed its safety is and how you can immediately find the data.

How to make a backup?
How to make a backup on Android? Android has basic built-in backup functions, and with the advent of new firmware they are regularly expanded. Such built-in functions are quite enough for the average user. In the “Accounts” category, you can simply leave marks for automatic highlighting, and when some problem arises or if the settings are violated, they will be recreated automatically as soon as the media is connected to the Internet.
However, it should be noted that in this case, applications downloaded from Google and installed on the gadget will not be recreated. To avoid this situation, you need to use special applications that make it possible to backup literally the entire media. A similar program is primarily Titanium Backup - the most popular application for backing up and restoring data after loss.
Using a computer
It should be noted that the easiest way to create a general backup of your own device is to backup your Android via a computer. This is very important, because we live in a time of technological development, and mobile devices have become an integral part of it; they contain a lot of important data that needs to be saved.
There are a lot of backup options via a computer. For example, you can restore via Google. Almost any Android device can interact with a working Google account. Then it’s simple: find the necessary settings in the menu (the “Personal” category), click the “Backup and Restore” command.
You just need to remember to check that all the boxes are ticked. If the gadget does not yet have the required entry, activate the “Backup Account” button, press it, and enter information from a previously existing entry.
To configure what the device should remember, go to the previous menu, find the “Accounts and Synchronization” section, where we select the items that need to be saved.

Synchronization must be triggered on the media; the key for this function is usually located in the upper section of the menu. Relevant instructions can be easily found on specialized websites. You can use other methods, understanding what backup is on Android. With knowledge of the basics, you can choose the appropriate option for saving data.
Flashtool
How to backup Android firmware using Flashtool? There are simple instructions consisting of several points:
- First you need to turn off the media itself. Then we activate the drivers, which can be found in the archive of basic programs. Open and find the scatter file. When it is not loaded, you can download it from any other media with a similar processor. Select with a tick only the first line of Preloader. And all screenshots in the gadget are clickable.
- Open the Memory Test section. Select only one line RAM Test.
- Activate the Start key and connect the non-working media to the computer, after which Flashtool will automatically switch the memory test to operating mode.
- We copy the information received from the memory test and transfer it to a notepad. Zero partitions are not needed (they are highlighted with a line in the screenshot).
- Switch to the ReadBack section and activate the Add button. Double-click on the highlighted line with your computer mouse. We write any file name (to avoid confusion, EMMC_USER is better) and the location where the memory block will be located.
- In the window on the screen we write three parameters, according to the data already found (see point 5).
- Find and activate with the Ok key. After that, press the Read Back key and activate the turned off gadget.
- As a result, separate blocks of flash memory will appear in the media, the largest of which is EMMC_USER (user region), several gigabytes in size depending on the brand of the media. To guarantee, the information can be flashed into the gadget using the SP Flash Tool - Write Memory program. The Android backup via Flashtool is completely ready. Now you don't have to worry about data safety.
Restore to general settings
Backing up Android without root rights is not a big problem. "Android" has a basic function to get a general backup of an Android gadget without root rights, as well as the technical capabilities to completely restore it. The maximum that is needed for this operation is a working computer and media running Android 4.0.
In addition, you can recreate and update the backup copy of your existing Android media using the Titanium Backup program. This is probably one of the most effective solutions for backup, but for this you need root rights.

Other options
It is much easier to use ADB utilities to create and restore a backup copy. This computer program for Android backup is available in the Google Android SDK, which is easy to download for free.
Let's start by activating the Java Development Kit (if not activated), since the Android SDK requires it. Download and activate the 32-bit Java Development Kit (Android SDK requires a 32-bit version, even when the gadget is running a 64-bit version of Windows).
You can then copy and activate Android. When the SDK responds that it is unable to detect Java, then perhaps you installed the 64-bit version, then install the 32-bit version.
Next is the next stage of backing up the Android firmware. Once you have resolved all the issues and successfully installed the SDK, activate Android SDK Manager from the menu on the Start screen. Check the Android SDK Platform-tools line and install to unpack the working options package for the platform that has ADB. When an error is found, you need to activate SDK Manager with administrator rights (touch the SDK Manager image on the screen in the Start menu and stop on the line “Run as administrator”).
Don't forget to enable USB setup on your own device. This can be dealt with using the developer toolbar in the basic Android settings.
Then connect your computer and your gadget using a USB cable. By this time, you need to activate the drivers for your gadget; as a rule, they can be found on the website of the smartphone manufacturer. As a rule, the computer installs the drivers itself. For example, you can activate Google USB Driver using Android SDK Manager, perhaps you can revive the gadget.
ADB examination
When working on a backup of the Android firmware, you must remember that the directory in which the Android SDK is located is shown at the very top of the Android SDK Manager computer window, not far from the SDK Path line.

You need to locate the adb.exe file in the platform-tools section. As a rule, it is located at C:\Users\NAME\AppData\Local\Android\Android-sdk\platform-tools.
Look into this folder and, holding down the Shift key, click on the right button of the computer mouse. In the window that appears in the context menu, click on the line “Open command window”. And in order to understand whether there is an adb connection with your gadget, run the adb devices command.
The name of your gadget should appear in the list of existing devices. If it is not there, the driver was probably installed incorrectly.
Using ADB
What a backup is on Android using adb commands can only be understood after completing the installation work. For a shared backup, run this command: adb backup -apk -shared -all -f C:\Users\NAME\backup.ab.
This action creates a backup copy of all existing applications and data on the SD card to the file C:\Users\NAME\backup.ab on a running computer. Write NAME in the line for the username of your device or select another space.
When you activate the command on your phone, you need to record the appearance of the backup copy. You can further protect your backup with a strong password.
Depending on the amount of information, the process may take a certain period of time.
To recreate the necessary backup, you need to run the following command: adb restore C:\Users\NAME\backup.ab.
Information will be highlighted on the screen confirming that the backup copy will replace all existing data on the media. If there is a password on the backup, then you must specify it.
In order to create a complete backup of Android without root rights, you can be an average computer user who understands the characteristic features of Android. I would like to believe that this feature will be in the Android interface in the coming years.

Synchronization with cloud services
To save basic data on the device (music, photos), just enable synchronization with cloud services. You can use standard Google Drive. You just need to set up synchronization once and no longer worry about losing all your data if your phone is stolen or broken.
You can use other services; cloud storage, as a rule, is available in all email clients. They differ only in memory capacity, which is also an important parameter. So, storage from Google offers 15 GB for free, you will have to pay for additional space. The largest tariff plan offers 30 TB for $300 per month.
A similar service from Microsoft makes only 5 GB available; for 50 GB you need to pay two dollars a month. Another service, Dropbox, can be synchronized with the Microsoft storage. Only 2 GB is given for free, but if you invite other users to the system, you can get additional space for free. Unlimited features will be available to the user for only 10 euros per month per user.

The largest storage is 50 GB - “Mega”. This is one of the most profitable services where you can store data without worrying about its security. True, this service has a peculiarity - if you forget your password, it will be impossible to recover it.
As the well-known IT wisdom says, system administrators are divided into those who do not make backups and those who already make backups. I think everyone has had to set up a phone/tablet from scratch at least once after updating or crashing. But it’s not at all necessary to do this if you have a saved backup. In this article we will look at different types of backup (backup) of the contents of Android devices for all occasions.
Introduction
Having received root on a smartphone, the average user begins to experiment with the device and install various interface modifications, themes, fonts, new kernels, firmware, radio and root applications. As a regular, long-time and active user of the 4PDA and XDA Developers forums, I can say that very often such experiments end in questions with the wording: “The phone won’t boot, what should I do?”
Even after reading the instructions very carefully, you can make a typo or press the wrong button, and then get a bootloop - an eternal boot of the phone with repeated bootanimation. In the worst case, you can get a “brick” - the phone will not turn on at all. This happens very rarely, and, frankly, you need to try very hard to, for example, kill flash memory. Usually, what users consider to be a “brick” can be successfully restored with the help of simple manipulations. And backup will help us a lot with this.
Basic backup functions that will satisfy most ordinary users are offered by Google itself. In your phone settings there is an “Accounts” tab where you can check the necessary boxes. After flashing or resetting the device to factory settings or activating a new phone, Android itself will restore contacts, history and tabs of the Chrome browser, Google Keep notes, photos, application data, calendar events, and so on. In the latest versions of Android, you can restore the desktop with all shortcuts and automatically install all previously installed applications.
However, Google can't backup everything. System and application settings will be reset, saved passwords (or rather, authentication tokens) will disappear, applications from third-party markets will not be installed again. Therefore, we need tools that can save everything. We'll talk about them.
WARNING
Most of the applications described in this article require root and BusyBox.
Backup of applications and their data.
I myself follow the “clean install” approach. When upgrading to new firmware, it’s easier for me to set up programs from scratch. And the appearance of bugs in this case is reduced to nothing, especially when moving to the next major version of the firmware. But many users find it more convenient to save application settings and restore them on new firmware. This is especially true for third-party programs that are not in the market. I will focus on the two most popular applications, with millions of downloads.
Titanium Backup
The most powerful tool for backing up, restoring, freezing and deleting applications along with their data (including system ones and those pre-installed by the manufacturer). Allows you to set up automatic backup on a schedule without closing applications, and transfer any application to an SD card. You can store different backups of one application, save SMS, MMS, call history, browser bookmarks, Wi-Fi access points in the form of an XML file. Can sync all backups to Dropbox, Box and Google Drive. Using this application, it is easy to make any user application a system application, add encryption, and link the application to the market after recovery (for further updates). A convenient feature is the creation of an update.zip archive based on a backup of applications and data, which can be flashed from the recovery console to restore applications and settings.
One of the most useful uses of Titanium Backup is to transfer applications and their settings between devices. As an example, I’ll show you how to make the popular WhatsApp messenger work on a tablet without a SIM card. When you search for a program in the market, the description page will indicate that this program is not supported on your device. Even if you download and install the APK, to activate the program you need to call the device, which a tablet without a SIM card (or LTE with a tariff without voice calls or a dialer cut out of the firmware) cannot do.
So, go to Titanium, look for the desired application, click on it and click “Save” in the pop-up menu. If you swipe left in the menu, you can call up additional functions. The same menu can be called up with a long tap on the application in the list. After running the script, a new entry about the creation of a successful backup will appear in the notification panel. For ease of use, I advise you to configure the program to upload backups to the cloud. Synchronization can be configured on the third tab - “Schedules”. Click “Start” on the “Synchronization with Google Drive” item, and a notification in the curtain will indicate successful completion.
On the tablet we launch Titanium and synchronize backups with the cloud. At the same time, the newly made backup from the phone is downloaded. WhatsApp will be at the very end of the list of programs. A crossed out name means that the program is not installed on the tablet. Click on the program and select “Restore” from the pop-up menu. All. You can launch WhatsApp.
Helium - App Sync and Backup
The main difference of the program is the ability to work without superuser rights (the application uses the standard backup manager, available in any Android starting from version 4.0. - Ed.). At the same time, some functions are reduced and a companion application is required on the computer. The program will allow you to backup your user dictionary, messages and call logs, and Wi-Fi access points. System applications cannot be backed up, even if you are rooted. Also, reservation may be prohibited by the developers of some programs. They will be at the bottom of the list. For example, WhatsApp cannot be backed up.
Helium remembers all the devices on which it was launched and allows you to restore backups separately on different devices. Backups can be stored on a memory card or in the cloud (Google Drive, Box, Dropbox), and can also be made on a schedule. Another feature of the application is that it is easy to transfer data between devices, for example, having started a game on one device, you can continue it on another.
IMEI
There are often cases when, after updating the firmware, cellular communications and the Internet stop working. This is a sure sign that the IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) has failed. This number is unique for each device and serves to identify the device on the network. If there is a failure, it may be reset and the device will no longer see the network.
To avoid such cases, I advise you to make a backup of the EFS partition containing the IMEI in advance: using programs from the market, manually through the console (adb shell) or on the device through a terminal emulator. It is worth noting that for different devices the partition table may differ radically depending on the chips used. In the case of Nexus 4, you need to enter the following commands in the terminal:
Backup IMEI:
Su dd if=/dev/block/mmcblk0p8 of=/sdcard/m9kefs1.img dd if=/dev/block/mmcblk0p9 of=/sdcard/m9kefs2.img
Repair IMEI:
Su dd if=/sdcard/m9kefs1.img of=/dev/block/mmcblk0p8 dd if=/sdcard/m9kefs2.img of=/dev/block/mmcblk0p9
The Nexus 5 does not have a dedicated EFS partition. Therefore, you need to backup sections 12 and 13, which contain not only IMEI, but also other data:
Su dd if=/dev/block/mmcblk0p12 of=/sdcard/modemst1.img dd if=/dev/block/mmcblk0p13 of=/sdcard/modemst2.img
Restoration is carried out by a similar command.
Photos and videos
After unsuccessful firmware update or, for example, damage or theft of the phone, the most unpleasant sensation is caused by the loss of captured videos and photos. After all, applications can be reinstalled, passwords can be restored if necessary, and photos, if you don’t protect yourself in advance, will be lost forever. And in the market there are programs for every taste for saving your photos and videos. Let's look at a few of them.
Google+
A standard program from the “good corporation”, pre-installed on all stock firmware. I’ve been using it for a long time and on all devices (currently the albums contain more than 10 thousand photos). Automatically syncs all captured photos with closed Picassa albums (soon the same feature will appear in Google Drive). Photos will be available on all devices logged into the same account. If you have Internet access, all photos can be viewed even on a new device by logging into your Google account. A nice bonus is auto-correction of some photos, creation of collages from similar photos and GIF animations from series of photos. “Auto-creatives” also automatically appear - a cut to music from many photos and videos taken on the same day. When you change the location where you take photos and videos, “Stories” and “Travel” usually appear.
Other options
- MEGA- provides 50 GB of storage by default, has flexible settings, a synchronization client for the computer and an extension for the Chrome browser. Different viewing modes, the ability to open folders for other users.
- Cloud Mail.ru- 100 GB for new users. It has a nice interface and a client for the computer.
- Dropbox- is interesting because it has a companion application, Carousel, which can not only automatically upload photos, but also clean your smartphone from those that have already been downloaded.

INFO
It is better to store important backups in the cloud or on your computer so that they can be used even after a complete wipe of the device.
Backup of arbitrary files
There are also various programs for backing up files on an SD card. In general, they have similar features and differ in interface or supported cloud services.
Foldersync
Material Design, support for Amazon Cloud Drive, Box, Dropbox, FTP, Google Drive, Mega, OneDrive, SMB/CIFS, WebDav, Yandex Disk. It has a built-in file manager, many settings, filters, and convenient planning. Ability to configure two-way synchronization, transfer hidden files, configure transfer via Wi-Fi / mobile Internet, Tasker support, PIN code protection, ability to synchronize subfolders.
DataSync
Ability to synchronize between devices via Bluetooth, schedule, application data, files and folders. Automatic two-way data synchronization will allow you to save game progress and automatically download it to all connected devices when data changes on one of them.
Dropsync
Advanced synchronization client with Dropbox. Uploading photos and videos, monitoring battery level, Wi-Fi/3G/4G/WiMax connections and adaptation according to user preferences, customizable auto-sync interval, plug-in for Tasker, ability to select synchronization mode: download only, download and delete, only downloading, mirror downloading and more.
Essentially, this is an analogue of the Dropbox desktop client with on-the-fly synchronization (as in the Linux version of the client, file changes are tracked using the inotify mechanism, so everything is synchronized at once, and not at certain time intervals).

INFO
For Linux/UNIX users, rsync backup for Android is suitable, which will allow you to send and receive files from a remote server via SSH. Has Tasker support.
Full device backup
Nandroid backup (from NAND - the type of memory used in modern smartphones) is a complete backup of the entire firmware along with applications, data and settings. The function is supported by TWRP or CWM. In addition, you can make a backup directly from Android using the Online nandroid backup program. The already discussed Titanium, as well as Nandroid manager, will help you recover individual data. First, let's see how to make a backup from the recovery console.
CWM
To create a backup, select Backup and Restore, and then Backup to /sdcard. Before clicking, you can select the backup format or free up unused data. To restore, select Backup and Restore and then Restore from /sdcard. If you select Advanced restore from /sdcard, you can specify the boot, system, data, cache, sd-ext partitions for recovery separately.
For greater safety, the resulting backup can be transferred to a computer. But there's a catch. The fact is that if the device has an “external” (real) memory card, CWM will place the backup in it and it will be available for saving on the computer using standard means (directory clockworkmod/backup/date-and-time-backup on the memory card ). Everything is fine here.
A lyrical digression, or a declaration of love for Nexus devices
If you look at the partition structure of Nexus devices using the adb shell busybox fdisk /dev/block/mmcblk0 command (you need root and installed from the BusyBox market), you can see the following picture (see screenshot “Partition structure on Nexus 5 and Nexus 4” ).
The aboot partition is the primary bootloader. It can be damaged if, for example, you flash the kernel or bootloader from another device or pull out the cord from the phone during the flashing process. In this case, the partition table crashes and the phone stops loading into the bootloader and recovery, and also stops responding to fastboot and adb commands.
An ordinary user thinks that it is a “brick” and takes the phone to a service center, where he pays more than a hundred dollars for a new one to replace the allegedly burnt board. In fact, in section 15 for Nexus 4 and section 11 for Nexus 5 there is a backup copy of the bootloader - abootb. This is one of the reasons that it is almost impossible to kill the Nexus, because the backup bootloader can be restored without problems.
Turn off the smartphone and turn it on while pressing the keys simultaneously
$ adb shell su
The partition table will be restored, and if necessary, you can then flash the desired bootloader.
However, in smartphones without a memory card slot or in the absence of one, the backup will be invisible to the user. This is because Android's internal memory mount points have changed since version 4.2 to support multi-user operation. The virtual (internal) memory card itself is mounted in /data/media, and the CWM backup is also located there. But the main user's data is in /data/media/0, and it is this directory that is then mounted as /sdcard. Therefore, the backup will remain unavailable using standard means and without root rights.
You can get a backup from /data/media using a file manager with superuser rights or by connecting your smartphone to your computer in recovery mode. Next, enter the command adb shell, and then ls /sdcard/clockworkmod/backup/ to search for the directory with the latest backup. We transfer the backup with something like this:
$ adb pull /sdcard/clockworkmod/backup/2015-04-20.15.46.18 \ "D:\Nexus5\Backup\Nandroid\2015-04-20.15.46.18"
where the numbers are the previously found backup, corresponding to the date and time of its appearance, and at the end - the path on the computer to store the backup, which can be arbitrary.
TWRP
To create a backup, click the Backup button and mark the required sections with crosses (not sure - select all). Additionally, you can remove encryption, enable compression, skip creating an MD5 hash and select saving to a USB - OTG flash drive. As a result, the backup will be in the /sdcard/twrp/backups/backup-date-and-time directory. Unlike CWM, it will be available regardless of the presence of a memory card. To restore, click Restore and select the one you need.

INFO
The market has a large number of programs for separate backup and recovery of SMS, calls, contacts, kernels, recovery, and so on.
Nandroid Manager
It is a one-stop tool to manage all your Nandroid backups. Using Nandroid Manager, you can recover applications and data, SMS, call log, Wi-Fi hotspots, saved paired Bluetooth devices, and user dictionary from Nandroid. The application sees backups created in both custom recoveries, and allows you to rename them and search for information in separate databases within the backup.
 Nandroid Manager Features
Nandroid Manager Features
Online nandroid backup
Allows you to make a backup on a device operating in normal mode, without rebooting into recovery. In the settings you can select the following options:
- Backup name - manually each time / by UTC time zone / by phone time zone / based on the firmware version number, including the time of creation.
- Backup type - CWM/TWRP with or without compression.
- Mode - normal (full) / selection of partitions for copying. When you select the latter, a list with choices opens.
- Where to save the backup.
- The number of backups for storage is from “all” to 10 (if full, the older ones are deleted).
- Saving Yaffs2 sections as Tar files.
- Excluding Dalvik Cache from backup.
- Excluding Google Music files from backup.
The program supports uploading backup files to the cloud, FTP or Google Drive. A customizable schedule for automatic backups is available, from “every day” to “every 30 days” with the option “only when the device is charging.” Additionally, Tasker actions are supported using the plugin.
Backup using ADB
The method, so to speak, is for geeks. We connect the smartphone to the computer, enable USB debugging. Next, we use the adb backup command, which has the following keys:
- -f FILE - location and name of the backup file to be created on the computer. If this parameter is not present, the backup will be created in the current folder called backup.ab. On Windows, paths with spaces and special characters should be enclosed in quotes.
- -apk | -noapk - whether or not to save the APK application in the backup. The default is not to save.
- -system | -nosystem - whether to save system applications in backup. The default is to save. Selecting -nosystem will prevent saving system applications when the -all switch is specified.
- -all - save all installed applications, including system ones, in backup.
- -shared | -noshared - whether to include application data and the contents of the memory card in the backup. The default is not to save.
- - here you can write a list of applications that will be backed up. Ignores -nosystem.
Accordingly, to perform a full backup, use the following command:
$ adb backup -f "D:\Backup\ADB-2015-04-20.ab" -apk -shared -all -system
After this, Now unlock your device and confirm the backup operation will appear in the console, and a notification will appear on the phone asking you to confirm the operation and set an optional password for the backup. The process of creating a backup copy can last more than forty minutes, so there is no need to be nervous. To restore, use the command “adb restore path-to-file”, for the example above it would be:
$ adb restore "D:\Backup\ADB-2015-04-20.ab"
We confirm the request on the phone, enter the password (if you set it during the backup) and wait for the recovery, which may take even longer than creating the backup itself.
INFO
You can find out the IMEI numbers of all your devices linked to Google (including old ones) on the page google.com/settings/dashboard by opening the Android list.
Conclusion
I hope this article will help you save time and nerves when experimenting with the device. And even the loss or theft of a phone will not be a tragedy if backups of photos and applications are stored in the cloud.
When it comes to creating a data backup or recovery quickly and reliably, many Android users wonder what and how, in this article you will find many ways how and how to backup and restore later!
Why backup?
1. Your personal Android may store a lot of information that is very valuable, which you cannot afford to lose, or for example, you are planning to move from one Android device to another! Of course, when it comes to Google services, for example, everything is very simple here, you entered your username and password, waited 2 minutes until synchronization with the Google server was completed and the data was all there, but with other applications you will have to suffer to quickly make a backup copy and restore.
Method No. 1 - backup on Android and restore using standard ADB tools
Thanks to Google, which took care of creating a backup copy, the method is not ideal but still better than none!
So what do you need for this?
2. Download the program from the ADB RUN website (from version 3.21.35 and later)
Method No. 4 - DataSync (root)
The DataSync program is suitable for those who need to back up application data, as well as instantly move them to another device. If you need to create backup copies of applications themselves, and not just their data and settings, then this application is not for you. Learn more about how this DataSync application works.
Method No. 5 - OBackup (root)
OBackup - Creates backups just like Online Nandroid Backup, only this time the application has an intuitive graphical interface, and you can also send the backup to a cloud drive. OBackup details.
Method No. 6 - Titanum Backup (root)
Method No. 7 - Helium (root/ root)
A very interesting tool for creating backups. The principle of operation of this application is similar to the operation of the ADB debugging tools; more precisely, it is based on this method, only with the ability to choose which application to create a backup for. This application does not work on Motorola
The Helium application can work without Root rights, but if you have them it’s even better (if you don’t have root rights, you need Android to your computer).
How to create a backup using Helium?
1. To get started, download the Helium app
If you do not have Root rights, then you will also have to download and install the add-on on your PC
You may also need to install drivers on your PC (for non-Root devices), which are presented on the PC add-on download page

Creating a r.k. in Helium on Root devices
Launch the application refuse from the offer to log into Google Disk, so this function does not work entirely honestly (backup, but restoration only works in the paid version of the application)

You can save backups to internal or external memory

Android includes a built-in feature to create a full backup of your Android phone without root, as well as a tool to restore it. All you need is a computer and a device running Android 4.0 (Ice Cream Sandwich).
You can also create and restore a backup of your Android device using the Titanium Backup utility. Titanium Backup is perhaps one of the best backup solutions, but it requires root access.
Installing the Android SDK
To create and restore a backup, we will use ADB (Android Debug Bridge) commands. This utility is included in the Google Android SDK, which you can download for free.
First, you need to install the Java Development Kit (if not installed), since the Android SDK requires it. Download and install the 32-bit version of the Java Development Kit (Android SDK requires the 32-bit version, even if you have a 64-bit version of Windows).
Next, download and install the Android SDK. If the SDK says it can't find Java, then you may have installed a 64-bit version, in which case install the 32-bit version.
After you have successfully installed the SDK, launch Android SDK Manager from the Start menu. Check the box next to Android SDK Platform-tools and click the install button to install the platform tools package that contains ADB. If you see an error, run SDK Manager as Administrator (click on the SDK Manager icon in the Start menu and select “Run as Administrator”).

Preparing the device
You must enable USB debugging on your device. You can do this from the developer tools in Android settings.

Now connect your PC and your device using a USB cable. You must have drivers installed for your smartphone; usually they can be downloaded from the manufacturer’s website. Install Google USB Driver via Android SDK Manager (Extras subfolder), it might work.
ADB check
Remember the path where Android SDK is installed. It appears at the very top of the Android SDK Manager window next to SDK Path.
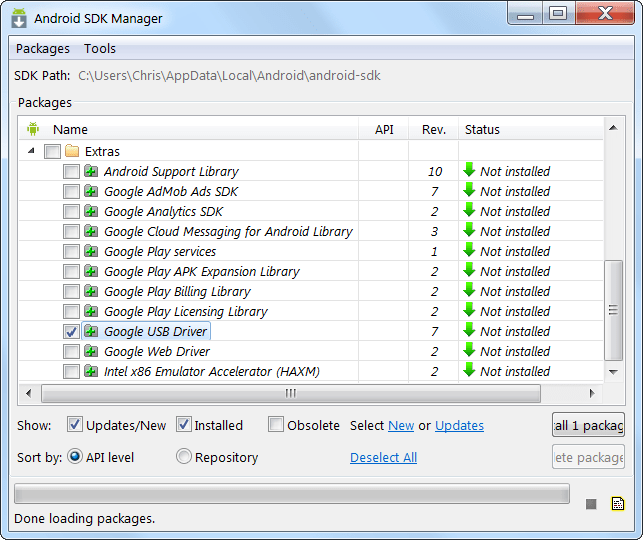
You need to find the adb.exe file in the platform-tools folder. It is usually located at C:\Users\NAME\AppData\Local\Android\Android-sdk\platform-tools.
Go to this folder and, holding down the Shift button, right-click on an empty space, select “Open command window” in the context menu that opens. To check the adb connection to your device, run the adb devices command.

Your device should appear in the list. If it is not there, then the driver is installed incorrectly.
Now you can use adb commands to create a backup copy of your device files. For a full backup, run the following command:
adb backup -apk -shared -all -f C:\Users\NAME\backup.ab
The command will create a backup copy of all installed applications (apk files) and data on the SD card to the C:\Users\NAME\backup.ab file on your computer. Replace NAME in the command with your computer's username or specify a different location.

When you run the command on your phone, you must confirm the creation of the backup. You can also protect your backup with a password.

Depending on the amount of data, the process may take some time.
Restoring a backup
To restore a backup, you need to run the following command:
adb restore C:\Users\NAME\backup.ab
A confirmation message appears indicating that the backup will replace all data on the device. If a password is set for the backup, you will need to enter it.

To create a full backup of an Android phone without root rights, you need to be an average user who understands the peculiarities of Android, but with the help of our instructions, even a beginner can do this. We hope this feature will be available in the Android interface in the future.