Review of software media servers. Your home multimedia server for TV
In this article we will configure a media server (DLNA) on a computer for a Philips TV. After setup, you will be able to watch movies, photos, and listen to music on your TV that is on your computer (laptop). All this using DLNA technology. This means that the TV can be connected to a computer via Wi-Fi. More precisely, the computer and TV must be connected to the same Wi-Fi router. Via network cable or wireless network.
I'll explain in more detail. Do you have a Philips TV (in this article we will talk about these TVs), with support (if you have a Smart TV, then there is definitely DLNA support). Your TV is connected to the Wi-Fi router (via Wi-Fi or cable). Also, a computer is connected to this router. We launch the DLNA server on the computer, open the necessary folders with videos, photos, or music, and simply start watching on the TV. Everything is over the air, without wires. It’s very convenient; you don’t have to write movies to a flash drive all the time. We simply access the computer, select the desired movie and watch.
Using the method described below, you can run a DLNA server on Windows 7, Windows 8, and even Windows 10. To launch and manage the server, we will use the free, simply excellent program “Home Media Server (UPnP, DLNA, HTTP)”. I recently showed how, where we launched a server using a proprietary program. Since Philips does not have such a program, we will use the “Home Media Server”. The program is really very simple and cool.
We will need:
- Philips TV with DLNA support. There must be a TV, or. I will show the example of Philips 43PUS7150/12 with Smart TV (Android TV).
- A computer that is connected to the same router as the TV. It can also be connected via a Wi-Fi network, or via LAN.
- The program "Home media server (UPnP, DLNA, HTTP)" for setting up a DLNA server.
You can do without third-party programs and configure everything using standard Windows tools. I wrote about how to do this in the article.
In fact, a server launched in this way will be able to see absolutely any TV: Philips, Sony, LG, Samsung, etc. Sony, by the way, already has models on Android TV. So, the instructions for them should also be suitable. Unless access may differ before viewing the contents of the DLNA server on the TV itself.
Setting up a DLNA server for a TV using the Home Media Server program
First, download and install the program "Home Media Server (UPnP, DLNA, HTTP)". I recommend downloading it from the official website: https://www.homemediaserver.ru/index.htm. Click on the button Download opposite the EXE version. The file size is approximately 35 MB.
Save the file, then run it and follow the instructions to install the program.
Launch the program using a shortcut on your desktop or from the Start menu. First of all, we need to configure access to files on the computer. We can open only certain folders, all local drives, or even removable media for the TV.
In the program window, click on the button at the top Settings. We are interested in the first tab, Media Resources. There will already be three folders open there. These are standard. To open access to all local drives on your computer, check the box next to Local disks. To open access to removable drives, check the box next to Removable drives.

If you want to open, for example, only one local drive or folder, then do not check these boxes, but click on the button Add. And in Explorer, select the drive or folder that you want to open for viewing on your TV. The folder will appear in the list. You can delete a folder by simply highlighting it and pressing the button Delete.

I think the meaning is clear. You can open only one folder, which contains, for example, your movies. And you can open all disks. I recommend checking the box next to Local disks. Then, the My Computer folder will be displayed on the TV, in which you can view all files.
At this point, the setup can be completed by pressing the button Ok. If you want, you can also go to the tab on the side Server, and change the name of your DLNA server. It will be displayed on the TV.

Click the button Ok to exit the settings.
To start the DLNA server, click the button Launch.

If your TV is turned on and connected to the router, then in the program window, open the tab Playback devices (DMR), you will see your TV. This means everything is fine. If the TV does not appear, then check the connection, and see the tips at the end of this article.

The program can be minimized. You can proceed to setting up DLNA on your TV.
Watch DLNA movies on your Philips TV from your computer
Press the button on the remote control SOURCES.

On the menu Sources choose Network (media). Or run the program Media from the Android TV menu.

Select the server running on your computer from the list.

If you have opened all local drives, then you will have a My Computer folder. Select it, all the disks will be there. You can open the desired folders and start watching movies, photos, or playing music from them. If you open one of the standard folders: Movies, Photos, or Music, then all available content will be there, sorted into different categories. To view content by folder, select Media Resource Catalogs.
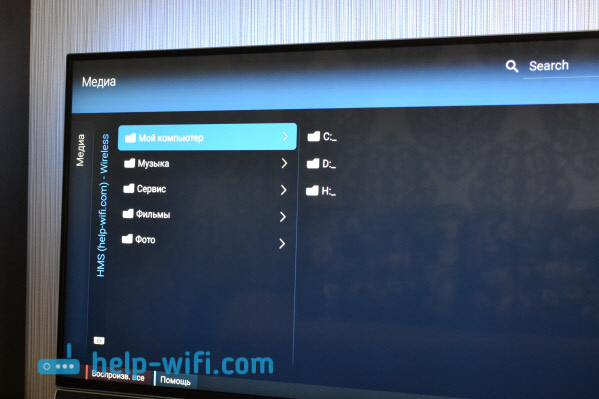
Select the folder with your movies and simply start watching the desired file.

That's all the setup. From the TV we got full access to the videos, photos and music that are on your computer. The program "Home Media Server (UPnP, DLNA, HTTP)" will prevent your computer from falling asleep and interrupting movie playback. You can also control viewing from the program itself on your computer. There are a lot of settings and possibilities there, I think you’ll figure it out.
Why is the DLNA server (files) not displayed on the TV?
The most common problem when setting up such a scheme is the lack of a running server on the TV. When files are from a computer, they simply do not appear.
In such situations, the first thing you should always do is check the connection of the TV and laptop to Wi-Fi, or the connection via cable. Perhaps one of the devices simply turned off. Turn off and on the TV. You can also restart your computer and start the server again. You can also try disabling the antivirus, which may be blocking the TV connection.
If a DLNA movie plays with delays, it's glitchy
In such cases, you most likely started watching a very difficult movie. And the router cannot cope with transmitting information. Typically, this problem appears on cheap routers and when connected via Wi-Fi. Large movies, in high quality, that do not want to be played via DLNA, are better watched from a USB drive or hard drive.
If, when opening a video, the TV says “Format not supported”
There are times when the TV does not want to play a video file. Most likely, the standard player simply does not support the format, there is no codec. In this case, if you have an Android TV, you can install VLC player from the Google Play Store. It can also play files from a local network. And most likely, it will play videos that were not opened by the standard player.
- DLNA - what is it and who needs it
- Windows media server dlna,
- A short overview of dlna server programs
- Home media server - the best among equals, or a headache for the user
- Setting up the server side
- Alternative and development
DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance)– a set of technologies for displaying various types of media content in real time by devices united in one local network. Initially, several companies (Sony, Intel, Microsoft, Samsung Nokia, Matsushita, Philips, Hewlett-Packard) developed this standard and also united into a group to create devices compatible with this technology. At the moment, there are more than 200 manufacturers producing compatible equipment.
home media server setup
In simple terms, this is a desktop computer, laptop, tablet, smartphone, TV and other “smart” equipment for viewing photos and video files, listening to music. Media content becomes common to every device on the local network. All gadgets must be on the same IP network and connected to each other either wired (Ethernet) or wirelessly (Wi-Fi).

How to set up dlna
All devices with dlna support are conventionally divided into two types: servers and media players. The former mainly store and provide others with access to content. The latter, for the most part, only reproduce the files the user needs. For example: a personal computer contains photographs; it can store and reproduce them both on its monitor and on the screen of a networked TV, tablet, or phone.
The division is conditional because now many mobile electronics can both store and display content. For example, smartphones with special software installed may well act as a server.
This technology is very useful for users with a large number of “smart” devices at home, as it allows you to store multimedia content in one place, rather than in the memory of each device. A very relevant feature for mobile devices that are significantly deprived of memory.
Windows and dlna
In the operating system from Microsoft, this technology appeared starting from version 7. However, it is hidden so deeply that it was quite difficult for the average user to find and configure it. In Windows 8, it became possible to use it to play video files on devices connected to the local network.
This is done by right-clicking on the file and selecting Transfer to... from the menu.

But before that, you still need to configure your home media server. In the “Control Panel” we find the “Home Group” item, in the window that appears, select “Create a home group”. Next, we will be asked to choose what type of file the homegroup can access.

In the next window we need the item “Allow all devices on this network, such as TVs and game consoles, to play shared content”, after clicking on which you will need to come up with the name of the media server and enter it in the proposed window.
At this point, the setup is almost complete and you can now play authorized files with dlna devices on your computer. To do this, each of them has certain points (AllShare, SmartShare...).
A description of how to use them is included in the instructions for use.
The software built into the system is easy to use and consumes less hardware resources. However, there is a high probability that the format of various types of multimedia files may not be understood by the player, since Windows transfers them as is. Third-party programs have been created to solve this problem.
Overview of dlna server programs
Of the many dlna media server programs, several stand out. They are all free, but provide additional features for a fee. All others are either highly specialized or simply provide information transfer on the local network and are an add-on to the Windows server. The programs listed below create a home non-Windows dlna server.
Codi– a project that grew out of XMBS. Due to its cross-platform, it works on Windows, IOS, Linux, Android.

It is a huge “media combine” that can find, transcode, download, and play a huge number of formats on the network. For this we are very much appreciated by users of TV set-top boxes.
A very bulky home media server, initially difficult to configure, it has a minimal number of add-ons. Different elements are downloaded and installed for different functions. In this regard, it is quite difficult to set up, but it has large support and Russian-language support too.
Plex– another multi-platform home media server. It has high-quality localization and a huge number of possibilities. But in this regard, it consumes a lot of system resources and is usually used for individual devices used as multimedia set-top boxes.

H.M.S.– a program with a huge number of functions, absolutely free. The main difference is the transcoding of files on the fly for playback even by outdated devices. It works only in the Windows environment, consumes significantly less resources, and therefore can be installed on a regular home computer. We will consider setting up this program below.
Server part of HMS (home media server)
The program interface is simple and setting up the first launch takes place in a few clicks. Before setting up your TV, first click the “Settings” icon, and on the “Media Resources” tab, add folders that can be viewed by connected devices. Adding occurs by clicking on “+” on the right side. For each folder, you can select a file type, which later helps when searching for them. =>

On the next tab “Devices” we add devices that are allowed to access files. It is very convenient to select the type of gadget from a variety of presets at the top of the window. This includes a large number of game consoles, TVs from different manufacturers, smartphones and routers. As a result, the settings will change for each selected device. If you check the box Add devices automatically, the program itself will determine the type of device and adapt to it.
In the “Server” tab we only need to enter a name for the created server. The rest can be left empty, unless of course there are several networks and connections at home.
The “Transcoder” item allows you to configure data transcoding so that any connected device reproduces the data, regardless of whether it supports it or not. The configured HMS processes the file in real time into a format supported by the TV.
The remaining tabs will allow you to fine-tune the program, which most users will not need at the initial stage. Therefore, close the settings and click the “Launch” button at the top of the window. After which the media server will begin scanning accessible folders and create lists of files that the connected dlna device will see.
In the main window of the program, you can also select the resource we need and use the right-click menu to transfer it to the player within the network. This is very convenient and there is no need to search for data using the dlna device itself.
The program has great user support. On the official forum, problems in the operation of the software with various devices are thoroughly understood, which helps to configure any equipment.
Setting up a client device
The process of setting up equipment for playing multimedia files varies for each device and is usually indicated in the instructions for use. The same point on any device is to select a server, the name of which we came up with during setup. And a request to connect to the network, a positive response to which needs to be made only once, will be considered allowed by the server in the future.
Alternative
Recently, there has been rapid development of cloud technologies. There are more and more devices that have access to the Internet. And storing data on physical media is no longer so relevant. Of course, a collection of films of several hundred copies is difficult to fit into any cloud service. And to increase the amount of allocated space you will have to pay. This requires an unlimited Internet channel with high speed.

Media resources are stored in the cloud, and access to it is provided to any device connected to the account. The advantage is that there is no need for a dlna server as a separate device. Simply put, you don’t need a constantly running hard drive with a large number of files. Access to files is available not only within the radius of the home local network, but also throughout the entire territory where there is access to the Internet.
With the development of Internet technologies, the home dlna server, dlna is giving way to “cloud” data storage, leaving the former the opportunity for the time being to exist in apartments that do not strive for modern technologies of users.
In general, the Home Media Server program is conceived by the developers as a home media server. But most often HMS is used as a DLNA server. It is ideal for this purpose and has many useful settings, often functioning even better than official programs such as LG SmartShare PC SW and the standard method of setting up DLNA via Windows Media Player. The idea is to allow the TV to play movies, music, pictures and other content directly from your laptop or computer. At the same time, they must be connected to the same home network, for the organization of which a router or router is usually used. After that, all that remains is to configure the program, and it’s done. You can download it on the official website http://www.homemediaserver.ru by clicking on the "Download" button.
Installing Media Server is as easy as shelling pears: unpack the archive and run “setup.exe”, where we agree to all the conditions and click the “Next” button everywhere. After successful installation and launch of HMS, the main program window will appear. When you launch it for the first time, select your TV from the list of devices (for example, LG TV). You can add media resources to which your TV will have access in the next window or in the settings later. In the program data backup and recovery window, click “Run” and “Close”.
HMS as DLNA server
We immediately go to the program settings. Here we have to configure our home media server like DLNA. To do this, in the “Media Resources” category in the very first tab “Directory List”, using the “Add” button, indicate the paths to the folders on our computer where the media files that you would like to see on an LG TV or other are located. After adding all the folders, click "Scan". Although we will set up auto-scanning of new media resources, new elements still sometimes do not appear automatically, and you need to scan using this button manually.
On the "Scanning" tab, it is important to enable automatic scanning of directories when they change and start the program, so that new media files are immediately displayed on the TV.
In order for Home Media Server to start when the computer boots, in the “Advanced” category you need to check the boxes “Start the program when you start a Windows session” and “Install the Windows Home Media Server service...”. Setting up HMS for the DLNA server is complete, click OK.
Next, select the “PC Connection” tab and click the “Next” button 3 times. Please note that in step 3 your home network is selected (wired or wireless, depending on how you connect the TV), otherwise select it.
In step 4 you should see your PC. If it's not there, restart the server, this usually helps. Next, select the device and go to the “Connected devices” item.
View Media
After the first connection, our device will be displayed in the last item of LG SmartShare - “Connected devices”. If it is not there, restart the server on your PC. For example, to watch movies you need to select the “Movies” folder, then “Media resource directories”.
Here you will see a list of folders added in HMS settings. Go to any folder and launch the movie. Sometimes the TV may write that "The file type is not supported." Don’t despair, this is a glitch, try to run it again and everything will work out 2-3 times.
Features of HMS
The advantages of a home media server from Serviio are as follows:
- on the TV you can see a clear PC folder structure;
- the ability to start playing media files on TV from the program itself on a PC. To do this, you need to select a file from the list and click on the green Play button, which is present if the TV is turned on;
- relative stability of operation (after PC SW DLNA from LG it’s just a fairy tale);
- a large number of settings.

Flaws:
- some confusion for beginners;
- Sometimes automatic scanning of new files does not work;
- Periodically you have to restart the server for the device to appear on TV.
Despite these shortcomings, HMS is ideal as a home media server, including DLNA. Details on setting up the Home DLNA server are in the following video.
Other options
The capabilities of the Home Media server reviewed do not end with DLNA. HMS can provide access to computer media resources using UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) technology and the HTTP protocol. This is more relevant for smartphones and tablets.
But this server can do a lot more for DLNA. For example, you can give access not only to computer resources, but also to streams of Internet radio and IPTV television. It is also possible to broadcast so-called podcasts from various online cinemas, such as hdserials.ru, hdkinoklub.ru and hundreds of others. There are also possibilities for transcoding media files of a format that is not supported on TV. How do you like this? All this will be discussed in the following articles, subscribe to our newsletter, as well as VKontakte and Twitter.
Owners of modern digital gadgets - smartphones, tablets, as well as high-tech TVs with Smart TV support - can create a real media server at home, with which they can access various types of multimedia content from different devices. How to use this opportunity in practice?
How a home media server works
What is a home media server? This is a system within which various devices connected to a network - computers, televisions (if they support the corresponding functions), mobile gadgets and other modern devices - can interact and exchange multimedia content. Another notable technology that can be used through a home media server is IPTV. That is, having built the appropriate one, the user will be able to organize something like a mini-TV studio at home.
How does a home media server work? As a rule, its structure assumes the presence of a main module responsible for storing files and media data, access to which can be organized from devices connected to a common network. This is usually a PC or laptop. In the hardware part, they are used to host files and organize procedures for exchanging them; in the software part, they provide the necessary functionality of the media server.
Features of DLNA standards
Media servers can operate using a variety of technologies and standards. Among the most common in the global IT market is DLNA. This is a set of standardized algorithms supported by most modern TV models, smartphones, tablets, set-top boxes, etc. DLNA capabilities are sufficient to solve most problems related to the distribution of media content. This standard, moreover, does not require complex configuration. All this, in fact, makes DLNA technologies in demand among users of digital devices around the world.
How to install an appropriate multimedia content management system? How to use a home media server based on DLNA algorithms? Let's study these questions sequentially.
Creating and configuring a home media server
The first thing we need to do is create our own home media server. The instructions with which such a problem can be solved involve the following basic steps:
Preparation of hardware components;
Software selection;
Network setup.
Let's consider the relevant aspects of creating a media server in more detail.
Hardware package
First of all, it is necessary to prepare the hardware, that is, the hardware of the future media server. As we noted above, the corresponding multimedia content distribution system requires the presence of a main module - in the form of a computer or laptop. The performance requirements for the corresponding device will not be strict: to perform the corresponding function of a media server, you can assign a device that may be outdated for running modern games and therefore is least often used by digital technology lovers living in an apartment.

It is enough for the computer to have a processor with a frequency of about 1-1.5 GHz and RAM of about 1-2 GB. In principle, it is possible to organize network operation with lower performance characteristics. The size of the hard drive depends on the actual needs of the user. If a person plans to use a media server to store movies in high quality and then distribute them over the network, then he will probably have to equip a PC or laptop, used as the main element of the corresponding infrastructure, with a hard drive of about 500-1000 GB.
Wi-Fi equipment
It is extremely important that the device in question supports Wi-Fi connections. Of course, it is quite possible to organize a functional media server using wired connections - but this is less convenient and usually takes more time. Most modern laptop models have a built-in Wi-Fi module. As for "desktops", this is not always the case, but the corresponding hardware component can always be purchased separately. It is inexpensive - about 700-800 rubles. No special installation effort is required - all you need to do is insert the Wi-Fi module into the PCI slot and install the drivers included with it, if necessary.

In order for all devices included in the home network infrastructure to communicate via Wi-Fi, you will also need a router. Theoretically, of course, you can connect one device to another directly - the corresponding wireless standard supports this function, but in this case the connection channel will not be as stable as when using a router, and in most cases it will be less secure due to limited support strong By the way, Wi-Fi routers are provided by many modern providers, so it is possible that the user already has the corresponding software component at his disposal. If not, you need to purchase one, and it must support the Internet connection standard you are using - for example, a fiber optic connection, Ethernet or ADSL.
Note that devices that are supposed to be used to access multimedia content distributed by a home media server must support the DLNA standard. But most often there are no problems with this - if we are talking, for example, about modern models of LG, Samsung, Philips TVs with Smart TV support. Regarding smartphones and tablets, modern models also, as a rule, integrate without problems with media servers.
Software
Another part of the home media server infrastructure is the software. It must be installed on a PC or laptop used as the main module of the corresponding system. Software for such purposes is available in a very wide range of varieties. It can be classified on two bases: programs created by brands that produce multimedia devices (for example, televisions), as well as solutions produced by third-party developers. So, in order, for example, to create a media server for Smart TV when using Samsung TVs, you can use the Samsung Allshare program. Similar solutions are produced by other digital technology brands.
Home Media Server Benefits
Among the most popular types of software from independent developers is the Home Media Server program, or “Home Media Server”. The instructions for using this software do not imply any difficulties in mastering. The necessary settings for the home network and media content management algorithms are carried out in the HMS interfaces easily and quickly. This program is also characterized by great functionality and stability.

HMS is a universal solution. Using it, you can integrate virtually any brand of TV and home media server - for Philips, Samsung, LG and other leading brands of digital equipment manufacturers, it does not matter what type of software the network owner uses. The program in question is fully compatible with the DLNA standards that we mentioned above. HMS capabilities allow you to organize shared access from various devices to files, as well as television broadcasts in IPTV format.
Features of TVersity
Another popular program used by many users to run a home media server is TVersity. What are its specifics? First of all, it can be noted that it is available in paid and free versions. The difference between them is not very big in terms of software functionality. The main distinguishing feature of the paid version is the presence of a subscription to some Internet channels.
TVersity's notable features include optimizing media sharing from a home network perspective. Thus, the transcoder, which is activated by the program, can produce video with a given bitrate - so that the corresponding media stream is displayed on the screens of receiving devices continuously, even if the network is slow. There are no problems with how to set up a media server using this software. Instructions for using the capabilities of TVersity are quickly mastered even by beginners in creating home networks.
Advantages of XMBC
Another notable program is XMBC. It was originally created for use with Xbox consoles. However, now this is a popular cross-platform solution that can be installed on PCs running Windows, Linux, Mac, and mobile platforms. This program is notable in that it can provide shared access not only to media files located on the hard drive of the PC used as the main module, but also to online media. Using XMBC, users can access pages of popular social networks and watch the weather forecast. Many users are also impressed by the fact that XMBC supports a large number of themes. A special xbmcRemote application is available for this program, with which you can configure your smartphone or tablet as a remote control for devices connected to your home media server.
Specifics of Plex Media Server
Another notable program is Plex Media Server. Many users characterize it as one of the easiest solutions to learn. Plex is also distinguished by its stability and versatility: it can be used to connect a variety of types of devices into a network. The versatility of the program is also reflected in the fact that it is equipped with algorithms for transcoding media streams. This feature allows you to avoid problems with recognizing content on different devices. Another important advantage of Plex is that it is cross-platform.
LinuxMCE Features
There is actually a separate operating system that allows you to manage home media servers - LinuxMCE. It can be noted that its functionality is not limited to support for DLNA standards. This operating system allows you to connect not only TVs, smartphones and computers, but also other electronic devices, such as cameras, IP phones, into a single network.

Which of the above solutions is best for managing a home media server? Each of them has undeniable advantages, very few have significant disadvantages. Most likely, the question will not be about the quality and capabilities of this or that type of software, but about the user’s readiness to master them, as well as his practical needs for specific program functions. So, if he needs basic capabilities - organizing shared access to video files, Internet television - a media server can be created under the control of HMS - a simple and easy-to-use program. If you plan to create a powerful infrastructure that involves connecting a large number of digital devices to your home network, you can pay attention to XBMC or even LinuxMCE.
Practical use of media server capabilities
So, we have decided what hardware and software components are needed to organize the network. Let's continue to consider algorithms that reflect how to create and configure a media content distribution system, as well as how to use a home media server.
It can be noted that using the capabilities of programs - at least those that we discussed above - does not involve significant difficulties. The first thing you need to do is install the appropriate software on your computer. The further algorithm of our actions will depend on what functions we want to use. Among the most popular of them among owners of digital devices is organizing shared access to media files from different devices, as well as watching TV shows using IPTV technology using devices included in the network.
Let's look at how to configure a home server to solve the above problems using HMS as an example.
Sharing access to media content in HMS
Among the main advantages of the HMS program, as we noted above, is versatility. With its help, virtually any device can be combined into an infrastructure, the central part of which is a home media server. For Philips, Samsung, LG and other brands, it does not matter what type of software is installed on the main network module.
To solve the problem associated with organizing shared access to media files - videos, photos, music - we launch the program, then select from the list of devices displayed in the main window the one with which we are supposed to launch files on the media server. For example, it could be a TV-enabled TV.

After this, you should specify the media resources that are to be distributed among the devices connected to the network. You need to go to the HMS settings, select the “Directory List” item, then “Media Resources”, and then, by clicking the “Add” button, you should specify the address of the corresponding files. As soon as these actions are completed, you need to click the “Scan” button, and then activate its automatic implementation so that the corresponding content is promptly displayed on the TV.
How to use a media server using TV? Very simple. You need to load an interface using the TV remote control, which is supposed to indicate the source of the TV picture - this could be the antenna itself, an Internet channel, a flash drive, or, as in our case, a media server created using the DLNA standard. The corresponding item should appear in the TV menu, and those files that we have marked in HSM as being shared will be available for launch. Modern TVs, as a rule, recognize the home media server without problems. For LG, Samsung, Philips and other brands, providing support for standards like DLNA is the norm.
Using IPTV on your home network
Another common problem solved by home network owners is organizing TV broadcasts using IPTV technology. The most important condition here is that the user has a subscription to the corresponding service of the provider (it is usually paid). When using HMS interfaces, setting up the media server in terms of using IPTV is also very simple.

You will need to download and install the VLC Media Player program on your PC - it will be used to work with the corresponding content. You need to link it to the HMS interfaces by going to “Settings”, then selecting “Media Resources”, then “Internet Resources” and specifying the folder in which the VLC program is installed.
After this, you need to upload a playlist of TV channels in m3u format to HMS - many providers allow you to download these files from their websites. After that, go to “Settings” again and check the “Internet television” option in the “Transcoding profile” item. After this, you need to restart the media server. Then you can start watching channels in IPTV format using your TV.
What are DLNA and UPnP?
The Integrated Digital Network Consortium (DLNA) is a group of companies that have come together to create a common, open standard for connecting devices. All devices that have DLNA support can automatically, while on the same network, be configured to receive from each other and view content.
What types of devices support DLNA?
DLNA-compatible devices include TVs, mobile phones, PCs and laptops, music players, game consoles such as Sony PlayStation 3, home media players, personal computers, Android phones, Blu-Ray players, tablets, wireless printers, camcorders, TVs flat screen, routers and HiFi systems. First of all, make sure that your device has this support. All DLNA Certified devices have a logo or sticker indicating that the product has been tested to meet DLNA requirements and is capable of connecting to other certified devices. Next, the device must have a description of the type of digital content supported (for example, audio, video, photos), as well as the type of purpose (for example, server, printer, player, etc.). A more detailed description of the accepted notation is at the end of the article.
Currently, The Digital Living Network Alliance's membership list includes most of the major players in the market, such as Intel, HP, Motorola, HTC, Microsoft, Samsung, LG and Panasonic. These companies create products that work well with each other. Only Apple remained on the sidelines and developed its own standard - AirPlay. So if you have a device from the Apple family, you won’t be able to include it in your media network consisting of devices from other manufacturers.
How does DLNA media server work on Windows?
DLNA devices are designed to be interconnected. Each device is assigned its own class depending on its purpose. For example, any storage device belongs to the Digital Media Server class. These are mobile phones that store photos, music and videos in their memory. Any device that can receive and play digital content from another DLNA device will be a Digital Media Player. This is your TV that can play videos, music and photos from other devices.
To create a home media server, you will need at least one DLNA server to store the content (for example, a laptop or mobile phone) and one DLNA device to play it back, such as a TV.
DLNA devices connect and communicate with each other through a configured home network. The layout of this network is probably similar to your home Internet network. In fact, a router is the central point of communication in a network and is used to connect devices to each other.
Here's a short list of what you'll need:
- TV with DLNA support
- at least one DLNA digital media server, such as a file server, laptop or phone
- router
- one of three to connect the receiver to the transmitter: Powerline adapters (for distributing the Internet via the power grid), Ethernet cables or a wireless adapter for connecting to your network.

Setting up a DLNA home media server on a Windows computer or laptop?
We have come close to the topic of setting up a home media server via DLNA. First of all, you need to connect a laptop and a TV that supports this technology (for example, Samsung with Smart TV) to the router. There are several ways to do this. This is discussed in detail in, but they are briefly listed below. Which one to choose is up to you, depending on how far the router is from your TV and other connected DLNA devices.
- Ethernet cable
If your router is close to your TV, an Ethernet cable is the easiest way to connect them.
Simply connect one end of the cable to the TV's Ethernet port and the other to the router's port. - Wireless bridge
If you have a wireless router, or your TV is far enough away, you might want to consider installing a wireless bridge to connect your TV to your router. The wireless bridge connects to the TV via an Ethernet port, and to the router via a wireless connection. Or, if your TV supports WiFi via a built-in or external adapter, then connect it to the router directly. - Via electrical network, without cables
Networking using a power grid is a great way to set up a network throughout your home. Installation using your home's electrical network is simple and safe. Since existing wiring is used, cables are no longer required for connections within the DLNA network. Adapters for connecting to a network outlet are produced by almost all manufacturers of network equipment. They are called Powerline devices. Next, you simply connect the plug of the router, TV and other devices to the power outlet as usual, but now all your devices will form a DLNA network
Some wireless routers, such as those from Buffalo Technology, are DLNA certified and are specifically designed for a DLNA home network.

Before you can transfer files from your computer, you must install the appropriate software on it. Options include Windows Media Player 11 or 12 (included in the new version of Windows 7) or VAIO Media Server (for Sony TV), AllShare for Samsung, LG Smart Share, Home Media Server, etc. After installing the software, you can select files to transfer to TV - photos, videos, music files, etc. How the transfer occurs depends on the software you're using, but typically it involves specifying a playlist, library, or files, or adding them to the appropriate folders.

Let's now look at the most popular programs that allow you to stream files from your computer to other devices.
Windows Media Player
To set up Windows Media Player to transfer files from your laptop to your TV, follow these steps:

SAMSUNG Allshare Software
You can download it here. More advanced compared to the previous program, but again only for Samsung. It is based on the *DLNA standard, and with its help you can share multimedia content not only on your TV, but also on many other devices that support the *DLNA standard: computers, tablets, camcorders, digital cameras, mobile phones, etc.
The operating procedure is as follows:


Now, for greater clarity, watch a video demonstrating how to work with these programs from Samsung.
Home Media Server - Home Media Server
This is another cool free program for organizing a full-featured media server from your computer, from which you can broadcast files to other devices included in the local network - not only a TV, but also a tablet with Android OS, for example. Its advantage is that it is suitable for any TV that supports network connections, for example the same inexpensive LG. You can download the latest version.
Let's take a closer look at how to use the Home Media Server. After installing it, you will be asked several times to set the basic parameters - here we click “Cancel” everywhere, but we do nothing, since we will configure everything later.
We get to the main program window.


In addition to viewing files, this program also allows you to broadcast streaming broadcasts from the Internet to your TV. But we'll talk about this separately...
I hope that now all blog readers have become clearer about what a DLNA media server is and how to connect various devices to it. Well, after carefully studying all this information and competent implementation, you can build something like this:

By the way, the phone can also work as a server - but more on that in a separate article about. You will learn how to connect to a home media server.
For a snack there are also many other delicacies - the most popular questions with answers, a glossary of terms and visual videos on DLNA. And don’t forget to subscribe to blog news using the form below the article so you don’t miss the next article in the DLNA series. It will focus on the universal cross-platform media server Xbox Media Center (XBMC).
Frequently Asked Questions
Are all TVs DLNA certified?
No, not all TVs support DLNA. To make sure yours supports the DLNA network, look for the corresponding logo on it.
What should I do if my router is located a long distance from the TV?
There are two options if your router is located far from your TVA and other devices
- DLNA: Connect via wireless bridge or electrical cable. This way you can connect your TV and devices to the router
- DLNA wirelessly. This article describes detailed installation steps.
Is it possible to connect other devices to the DLNA server via WiFi?
Some DLNA devices have built-in WiFi functionality. The method of connecting via WiFi will depend on the device itself. You may need to enable WiFi or Network Sharing in order to connect to your router (and DLNA network).
My TV does not connect to the media server. What should I do?
- Check the cable and connections between the TV and the router, and between the DLNA devices and the router.
- Check your network setting on your TV. Connecting a TV to the network is described in detail in a separate article, the link to which I provided above.
Which devices support DLNA?
There are a number of devices that support DLNA. Visit the Integrated Digital Network Consortium (DLNA) website
My BRAVIA TV does not recognize some devices. What should I do?
If your BRAVIA TV does not find content on another device, there may be the following reasons:
- Your TV or other DLNA device is not connected to the network.
- The problem is with the router or the network.
- The other device does not support DLNA or is not a Digital Media Server, in other words, it does not have memory to store files.
- Your PC or laptop does not have the appropriate DLNA server software installed.
- Depending on your network settings, you may need to disable the firewall feature on your laptop. You should be aware of the risks associated with this activity. They are entirely your own responsibility. If you don't know what to do, seek professional help.
Which network setup method is better - cable or wireless?
It all depends on the distance of the network components and how desirable it is to have visible cables in the house. A cable network, however, may perform slightly better than a wireless one. A few more tips:
- Try to avoid complex network setups with multiple subnets and hubs as this may impact the performance of your DLNA network.
- If you want to be able to stream HD video files, we recommend using a network speed of at least 200 Mbps for more stable performance.
- When choosing an Ethernet cable, choose Cat5e over Cat 5 as this will allow your network to reach faster speeds.
Can I rotate images when the TV is connected to a PC?
No, you cannot rotate images on the screen. You must rotate the image on your laptop or other device before it can be displayed on your TV screen.
Photos appear distorted on the TV screen. Why?
As you enlarge the photo, the image quality may deteriorate. For optimal quality, display photos at their native resolution, even if they don't fill the entire screen.
My photos don't fill the entire TV screen?
Images may not fill the entire screen. It depends on their resolution and format. For optimal image quality, do not change the native resolution.
What file types are supported by DLNA devices
It depends on the device itself. View your specific device's DLNA certificate
or visit the DLNA website. Depending on the network device, some files may be converted before
transmission. Below is a list of files that are typically supported by DLNA devices:
- Images: JPEG, BMP, PNG, GIF, TIFF
- Audio: MP3, WAVE, AAC, AC-3, Ogg Vorbis, LPCM, AMR, WMA*
- Video: AVI, FLV, MPEG2-PS, MPEG4, H.264 SD, WMV, WMA
Can I store files on my TV?
No, your BRAVIA TV is a DLNA media player. This means that it is capable of finding and playing files from DLNA media servers that contain content. Your DLNA-enabled BRAVIA TV guarantees an amazing audiovisual experience when watching movies and listening to music. In every sense, the TV is the best DLNA media player.
Do I need to install additional software on my PC or laptop to transfer files? Where can I find this software?
Yes, in order for your PC or laptop to transfer files within a DLNA network, software installation is required. In some cases, such as Windows Media Player 11, the required software is already installed. Below are programs that allow you to share files within a DLNA network that you can download for free: The connection between your DLNA device and your router may have been lost. Check cables and connections. To check the connection between your DLNA device and your TV, you can also run an automatic diagnostic test, which is different for each model.
Sometimes the video quality when streaming wirelessly is quite poor. Why?
The quality of your wireless network connection can vary depending on the distance between the bridge and the router, any interference in the room, and the quality of the wireless router itself. To improve picture quality, use a wireless router that supports 5GHz video streaming and place the router as close to the wireless bridge as possible.
DLNA Technology Conventions
When using DLNA connections, you can create a connection between any devices that work with this standard, and each of them can act in different roles. To refer to them precisely, a number of terms are used, which are described below.
The first group of device connections, which are used mainly in the home, is called HND (Home Network Devices)
 | DMS (Digital Media Server) - media server. These are devices that are the source, that is, which contain the files that we want to watch on another device. This could be a computer with the special software listed above installed, or a NAS device that has DLNA support. |
 | DMP (Digital Media Player) - media player, or DLNA client. These are the devices that receive content from the media server and can either play it or transmit it to another device, acting as a media renderer. These are TVs, game consoles, independent monitors, home theaters, etc. |
 | DMR (Digital Media Renderer) - media renderer. A device capable of playing content received through a media controller, which in turn transmits it from a media server. Usually the same ones that can do this are those listed above in media players. |
 | DMC (Digital Media Controller) - media controller. Allows you to find files on the media server and transfer it for playback on the media renderer. These are tablets, smartphones, digital cameras with support for WiFi connections |
| DMPr (Digital Media Printer) - devices that provide printing services for others - these are also printers. Media players (DMP) and media controllers (DMC) are capable of transmitting printed information to them. |
Another group of devices - MHD (Mobile Handheld Devices) - are portable devices capable of transmitting and receiving content - mobile phones, tablets, smartphones, video cameras, cameras.
 | M-DMS (Mobile Digital Media Server) - mobile media servers. Gadgets that are capable of distributing content stored on them to mobile players (M-DMP), media renderers (DMR) and printers (DMPr). these could be mobile phones or portable media players. |
| M-DMP (Mobile Digital Media Player) is a mobile media player capable of playing video from servers - stationary and mobile (DMS and M-DMS). This role is played by phones, PDAs, | |
 | M-DMU (Mobile Digital Media Uploader) are portable gadgets that can upload files to servers. For example, digital cameras, camcorders or phones. |
 | M-DMD (Mobile Digital Media Downloader) - portable devices that can find and download media content from DMS and M-DMS servers (mobile phones and media players) |
 | M-DMC (Mobile Digital Media Controller) are portable media controllers that have the ability to find content on media servers and broadcast it to DMR media renderers - phones and PDAs. |