How to remove broken files from your computer. I can't delete a file or folder from my computer
Deleting a folder in the operating room Windows system 10 – simple procedure. However, there are times when it is not possible to remove a directory. It is not deleted, blocked or given special rights. IN in this case Can you give me some advice on how to delete a non-deletable folder in Windows 10?
Reasons why a folder cannot be deleted
If a directory is not deleted in Windows 10, there are many reasons for this. Let's consider only the main ones:
- The folder or file is blocked by the antivirus. Relevant if the directory has been quarantined or the file has been sent for treatment (waiting for an update of the anti-virus databases).
- The file is being used by the system.
- Only the administrator has rights to the file.
- The directory is in use by another program.
- Another user is using the folder or file by local network.
- The folder is write protected.
These are the most common reasons why a folder or file cannot be deleted in Windows 10.
Different ways to delete folders in Windows 10
Before using programs to delete folders and files, you should check standard methods for performance. The file or folder may be in use by the program. Therefore, we restart the PC and try to remove it again. If this method does not work, reboot into Safe Mode and delete the directory.
Method No. 1. By using free program Unlocker
The Unlocker program is designed to unlock and delete folders and programs. Its usage is as follows:
- Launch and install the software. Right-click on the file that cannot be deleted and select Unlocker.
- Then select the file and click “Delete”.
Method number 2. Via file manager
The most popular file manager, which is installed on almost every PC, is Total Commander. To delete a file through this manager, you should follow these steps:
- We launch the program and look for the file to delete. Press F8 or the special button on the toolbar.

- The file has been deleted.
Method number 3. Renaming the file
Often a folder cannot be deleted because it is being used by other programs. Therefore, you can right-click on it and select “Rename”. After assigning a new name, the folder or file will be available for deletion.
Method number 4. By stopping the process and services that are using the file or folder
If the system blocks deletion of a file or folder, it means that the item is being used by some program or service. Therefore, we call the “Task Manager” and remove all processes and services that are associated with the directory.

It's also worth checking the Startup tab to rule out the possibility of using the file from Windows 10 itself.
Method No. 5. Using bootable media
- Boot from the installation media.
- Press F10 to open the command line.
- Enter “del file path” or “rmdir /s folder_name”.
- Afterwards we boot in normal mode.
Method number 6. Granting permissions on a folder
- Right-click on the folder and select “Properties”.
- A new window will open. Go to the “Security” tab. Select your user. Click on the “Advanced” button.

- In the new window, select the user to whom you need to grant rights to delete the directory.

- Check the “Replace owner of subcontainers and objects” checkbox.

- Next, we grant access to the rights to the folder. Click on the “Add” button.

- Then we put the marks that grant rights to the folder.

- Check the box “Replace all permission entries of the child object with those inherited from this object” and click on “Disable inheritance”.

- In the window that opens, click again on “Replace all permission entries of the child object with those inherited from this object.”

- Now we delete the directory.
This method is suitable if the rights to the object belong to another user and access is blocked.
If methods for deleting a folder that cannot be deleted in Windows 10 did not help solve the problem, you should check your PC for viruses and malware.
Also, see the video for ways to delete directories that are not deleted:
Often, when trying to uninstall a program, users are faced with the fact that the program is not uninstalled. When trying to uninstall a program through the Control Panel, the user receives an error that interrupts the uninstallation process. After which the program remains on the computer.
If you also don't know how to remove a program that won't uninstall, then this article should help you. Here we will look at three simple and effective ways solutions to this problem.
Method number 1. Stop all processes that are associated with the program.
If the program is not uninstalled, then most likely it is in at the moment works. In order to stop the program, open “ ” (for example, using the key combination CTRL+SHIFT+ESC) and go to the list of processes. In the list of processes you need to find those processes that are associated with the program and stop them.
If you have Windows 8 or Windows 10, then you need to right-click on the process you want to end and select “End task” from the menu that appears. On Windows 7 and older Windows versions, the menu item you need will be called “End Process”.
After all processes associated with the program have been stopped, you need to try to remove the program again. If this method If uninstalling the program did not help, try restarting your computer and try again. Perhaps something is frozen on your computer and thus blocked the program from being uninstalled.
Method number 2. Use a special program to remove programs.
If the program is not removed even after a reboot, you can try to remove it using special program. Most popular program this kind is . This program allows you to remove any other programs. Moreover, uninstallation is possible even in cases where the uninstaller does not work or the program is not displayed in the control panel.
Use Revo Uninstaller simple enough. First you need to run this program and wait until it scans the computer and displays everything installed programs. After this, you need to right-click on the program you want to remove and select “Delete”.

After this, a window will appear in which you need to select how to remove the program. In most cases, the Moderate option will do.

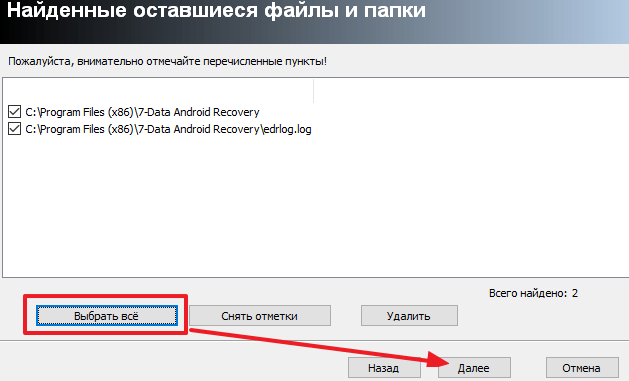
Here you can click on the “Select All” button and confirm the deletion by clicking on the “Next” button.
Method number 3. Uninstall the program through safe mode.
If none of the above helps you remove the program, then you need to boot your computer into and try again.

IN safe mode Only the main components of the operating system are loaded; other programs that may block uninstallation are not loaded. Therefore, in safe mode, deletion should proceed without problems.
Everyone has unnecessary files that they then delete, but what to do if folder is not deleted. There is a problem in which the OS does not allow you to get rid of unnecessary folder or writes that the file is open and cannot be erased.

Causes of the problem
You need to understand why the folder is not deleted:
- The antivirus application was blocking the data. If the antivirus considers the file infected or does not trust it, the program quarantines suspicious data and offers to disinfect the code. If treatment is delayed, the antivirus simply blocks the user from all access to data.
- The folder is used by other programs. You need to remember if there is software that can use this file. If there is, close the applications and delete the file. If that doesn’t work, go to “Task Manager” and check to see if the application is active.
- To clear a folder, administrator rights are required. When working under account with limited privileges, log out and log back in with administrator rights, and try to get rid of the folder again.
- The file is being used by someone on the local network. Wait for it to finish and clean up.
- The OS uses the data. Restart or try clearing data in security mode.
How to delete a folder that won't delete
When deleting a folder, the system gives us a window in which it writes the reason for the rejection of the uninstallation. There are different arguments, but one of them is that the data is involved, you will have to make it free before uninstalling it.

We do the following:
- In Windows 7 and XP, press Ctrl + Alt + Del, and in Windows 8 and Windows 10, Windows + X. Go to the “Task Manager”.
- We look through the processes and find an application that can potentially use the folder.
- We delete the file itself.
- When the file is used by the explorer.exe process, launch the console with administrator rights, cancel the task by entering the full_path_to_the_file for cleaning in the del line.
Return to the desktop, you can do this: run explorer.exe, to do this in the task manager select “File”, “ New task" and "explorer.exe".
Removing a locked file via bootable media
If a folder on your computer cannot be deleted, there is another method to get rid of it. You need to run from a LiveCD or recovery disk. Windows flash drives. When using the disk we can use both graphical interface, and the console.
The first step is to get an idea of the directories on the disk using the dir command, then use del path_to_file.

When using a flash drive or disk, press Shift + F10 to enter the console. Select “Restore system”, the link is in the installation program.
It is better to always check the drive letter from which the folder is being deleted, as they do not always match those displayed in the system.
A program for deleting folders that cannot be deleted – Unlocker
Folder not being deleted from desktop? - the Unlocker utility was created precisely for such a case. The application is free, it helps to detect all processes and locked files, and makes it possible to delete data. In the utility, you can rename files and extensions, as well as move a locked file.

Removal unnecessary file happens easily:
- Install the program.
- RMB click on the file.
- Select "Unlocker".
- Click delete and confirm by clicking “OK”
When a folder is locked, another window appears. In it, first click on “Unblock all”, and then “Delete”.
The folder is not deleted, what should I do?
Let's try to delete it using file manager - Total Commander. This manager allows you to bypass some restrictions.
We perform the removal:
- Load the FAR manager or Total Commander.
- After installation, look for the folder in the list.
- Click Delete.

The advantage of the manager is the detection of hidden and encrypted data. If the folder is not deleted, open it in the manager and look for hidden files, they are the ones who interfere. To correct the situation, go to “Task Manager” - “Processes” - find the file - click “End Process”. After this we delete the section.
Delete using autoload
So, open “Start”, click “Run”. Enter msconfig and click OK. “System Setup” will be displayed. Go to “Startup” and find a file that is not removed.

Not finding the folder in this list, click “Disable all” - “Apply”, “Close”. A notification will appear that the changes will take effect after a restart. We reboot and try to delete the folder.
Removal using short names
Another method is to use a short name, because it may contain invalid characters. We go to the folder, to find out what the short name should look like, enter the command DIR /X or DIR /X /N, it will show all the files with their short names. IN short name 8 characters are allowed per name and 3 per extension. 
Press DEL to clear the folder by short name.
If you still have questions on the topic “What to do if the folder is not deleted?”, you can ask them in the comments
if(function_exists("the_ratings")) ( the_ratings(); ) ?>
Surely you have encountered a situation where from a computer can't delete file: a window pops up with an error warning, and the file quietly remains in its old place. How to delete a file that won't delete?
Most often, it is not possible to delete a file because it is open in some program: usually applications block operations with files that are currently open in them. For example, you want to delete text document, open in Microsoft Word. Or you watched a movie and after watching it decided to delete it, but did not close the media player. In this case you need close the corresponding application and try again to send the file to the trash.
If even after this you are unable to delete the file, it is possible that Application related processes still remain in RAM computer: the application seems to be closed, but the system does not consider it as such. There are two options here: either “kill” the corresponding process through, or simply restart the computer. If you do not know what a task manager is, or have a very vague idea about it, it is better to resort to a reboot.
Sometimes the reason for the inability to delete a file normally may be an incorrect name (use of invalid characters in the name). This happens infrequently (usually the system will simply not let you name the file “incorrectly”), but it does happen. This can happen as a result of a malfunction of the program in which you opened/edited the file, or when unpacking the archive. Try renaming the file, perhaps after this you will be able to delete the file that is not being deleted.
If previous methods were ineffective, it may help deleting a file in safe mode. To boot into, you need to restart the computer and when you reboot, until the Windows logo, press the F8 key (to be sure, it’s better to press and hold). From the boot menu, select the Safe Mode option and press Enter. After loading the operating system, delete the “stubborn” file. An alternative to booting into safe mode can also be (the disk with the operating system).
But it happens that even in safe mode or when booting from disk, you still cannot delete the file. What to do? To remove particularly “unruly” files, you can use special utilities . One of the most famous such programs is Unlocker. This free utility unlocks files used by system processes, after which they can be safely deleted, moved or renamed.
The program works on both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows. She integrates into the context menu every element of the operating system (shortcuts, files, folders, etc.), so you don’t even need to launch it specifically to delete a file. The utility is available in 40 languages, including Russian.
To delete a file using Ulocker, download the utility from the program’s official website (you can choose 32-bit, 64-bit, or Portable version) and install. Now in context menu that appears when you right-click on an object should appear Unlocker item(in the 64-bit version this may be a sub-item in item X64).
If you are unable to delete the file, right-click on it and select Unlocker. A window will open with a list of processes blocking access to the file. Select the action you need to perform on the object (delete, rename, copy or move) and on the process (delete, unlock, unlock all processes). Sometimes, to permanently delete a file using Unlocker, you may need to restart your computer.
As you can see, there are several ways to delete a file that won't delete, and at least one of them should definitely work. By the way, sometimes viruses in the system prevent you from deleting a file, so It wouldn't hurt to scan your computer additionally antivirus program . It definitely won't get any worse.

From time to time, users encounter a problem when, after uninstalling a program, its remnants interfere with the operation of other programs or even the operating system.
This problem can manifest itself in different ways. For example, when installing new version or a program from another manufacturer, a message may appear that an old version of it (or a product from another manufacturer) was found on the computer, after which the installation process is interrupted. There are also cases when, after deleting a program, the context menu items of the deleted program remain in the Explorer context menu. Trying to run them results in an error.
This is due to the fact that there are traces (remnants) of the deleted program in the system, which interfere with work. They can be located both in the system registry and on disks.
Most often, antivirus users encounter this when, when switching from one antivirus package to another, a message appears stating that a version from another manufacturer is already installed on the computer. After this message, the installation process is interrupted.
How to correct the situation and remove the incorrectly deleted program?
1. Check the list of installed programs
First, we need to make sure that we really uninstalled the program. Although this is an obvious step, there are times when an app next to it in the list is mistakenly deleted. To eliminate this misunderstanding, you just need to check the list again.
To do this, launch the program removal tool and try to find there the name of the application that we want to remove. If it is not there, then move on.
2. We are looking for special removal utilities from manufacturers
When it comes to antiviruses or security tools, the developers of such programs often create specialized utilities for complete removal own products. As a rule, they are called something like this: %AntivirusName% Removal Tool. Instead of %AntivirusName% you need to substitute the name of the antivirus product.
Such utilities are precisely designed to completely remove a product from the system. And antivirus developers try to keep such products up to date, because users often need them. It is recommended to use them first if you want to remove antivirus solution fully.
Below is a list of links to such utilities for several popular antivirus solutions.
3. Removing remnants of deleted programs in the Reg Organizer uninstaller
If we are not talking about antiviruses, but about simple application program, that is, there is a chance that data on traces (residues) is available in the database of the program removal tool in Reg Organizer.
To do this, launch Reg Organizer and go to the uninstall tool. On the left side panel there will be an item “Traces of already deleted programs”.
If after the name of the item you see a non-zero value in brackets, then the Reg Organizer utility managed to find the remains of some programs. Check to see if the program you want to remove is among them.
If deleting remnants through Reg Organizer did not help or remnants for the program you need were not found, then go to the next point.
4. Manually search for leftovers on the disk
Now let's move on to manual methods searching for remains. First, let's check the disks for traces of the program that we want to completely remove from the system. To do this, we will use regular Explorer (or any other file manager convenient for you).
C:\Program Files\ and C:\Program Files (x86)\
These folders store the main working application files.
We need to find and delete the folder with the program name. Just go through the folders sequentially Program Files and when you find the one you need, delete it.

When doing this, you need to remember the name of the product manufacturer, because sometimes they place program folders in shared folder with the name of the manufacturer.
%AppData% and %LocalAppData%
These folders are used to store files that are created while the application is running. It could be configuration files for your system, logs and more.

To open them, just enter address bar Explorer %appdata% or %localappdata% and press Enter. operating system will automatically redirect you to the appropriate disk folder in your user profile.
We open the %appdata% and %localappdata% folders sequentially in Explorer and look inside these folders for the name of the manufacturer or directly the name of the product whose remains we want to delete.

Most often, AppData/LocalAppData first contains a folder with the name of the manufacturing company, and already in it there is a folder with the name of the product itself.
Some programs are installed entirely in %AppData% instead of Program Files.
Once you have found the product name folders in AppData/LocalAppData, simply delete them.
5. Manually searching for traces in the registry using Reg Organizer
In the system registry you can also find many traces of programs that were deleted a long time ago. To find them, launch Reg Organizer and select the “Registry Editor” tool.

On the right top corner There is a line for entering a search query. There we will enter the name of the program or the name of the manufacturer. But first we need to set up the search so as not to get a mountain of unnecessary keys, among which it will be difficult to find anything.

Open the search settings and leave a checkmark only opposite the “Key names” item in the “Where to search” block. This will give the program a command to look for matches only in the names of the keys, which will significantly reduce the number of entries in the search results and simplify working with them.

As soon as the settings have been changed, enter search query in the form of the name of the manufacturer or the name of the program (it’s better to start with the first) and start the search.

As a result, you will receive a small list of registry keys, the names of which contain the name of the manufacturer's company or the name of the program itself. You need to find those that satisfy the following construction:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\ %Company name%\%Program name%
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\WOW6432Node\ %Company name%\%Program name%
HKEY_USERS\%NUMBER-WITH-HYPHEN%\Software\ %Company name%\%Program name%
HKEY_USERS\%NUMBER-HYPHEN%\Software\WOW6432Node\ %Company name%\%Program name%
Designations:
%Company name%— the name of the company that produced the program, the remains of which need to be removed. Doesn't always exist. Instead, there may be a %Program Name% field.
%Program name%— the name of the program whose remains need to be removed.
%NUMBER-WITH-HYPHENS%— user identifier in the HKEY_USERS key.
Those keys that satisfy the above structures must be checked and deleted using the context menu (called by the right mouse button).
You can also check and, if detected, remove references to the remote program in the keys located at the following addresses:
\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\
\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\
Deleting data through the editor registry Reg Organizer is produced with the obligatory creation of a backup copy, which, if necessary, can be restored through the “Undo Changes Center”, which launches in the lower right corner of the main window.
6. Automatic registry cleaning in Reg Organizer
The last step in searching for traces of a deleted program in the registry is automatic cleaning using Reg Organizer. The utility analyzes key registry sections and looks for links to non-existent/ deleted files to then remove them correctly.
This is useful in cases where remote program recorded in startup, context menu, file extension associations and other similar sections.

Registry cleaning is carried out completely automatically and therefore does not require user intervention. You just need to be patient while the utility conducts an in-depth analysis system registry looking for links to deleted files and folders.
When you delete keys while cleaning the registry, Reg Organizer automatically creates backup copy deleted data, which can be restored if necessary through the “Undo Changes Center” (opens in the lower right corner of the main program window).
This procedure is performed last. This is due to the fact that it searches for links to deleted files. If you first clean the registry and then delete files, traces will remain in the menu, startup and other places, since the files were present on the disk at the time of cleaning the registry.