Official program for overclocking intel processor. Optimizing CPU performance: CPU Control utility
There are two most popular ways to overclock a processor. Using UEFI/BIOS or using software running on the operating system. The second method is simpler and allows you to overclock as needed using specialized utilities.
Useful tools
Before overclocking, you should stock up on tools that allow you to view all the necessary parameters of the motherboard and processor and control them during operations. A universal example of such a tool is the program CPU-Z. It works on Windows and Android operating systems. Below in the picture, as an example Intel Core i5, you can see what characteristics this program can read. The program is constantly updated, modern processors are added to it, and it will cope perfectly with the latest models Intel Core i7 And AMD Ryzen.
Despite the fact that overclocking is planned to be carried out using software, it would not be superfluous to first update the BIOS to the latest version. In any case, this will add functionality to the motherboard.
Well, it goes without saying that you must be sure that the cooling system of your electronic friend can cope with the increased loads and is also ready to accelerate.
Having completed these preliminary activities in advance, you can begin to explore the capabilities of specialized software.
SetFSB
The first program with which we will begin to study overclocking software will be SetFSB. As the name suggests, it is intended to overclock the processor on the system bus. You can download it on the official website. This utility is small in size and comes in the form of a zip archive. Having unpacked the archive, let's look at its contents, which are presented below.

In the program folder you can find text file setfsb.txt. By opening it, you can study the list of motherboards with which it can work. It is worth studying it carefully to find your model and make sure that when you run it on your computer, you will get the expected result.
During startup, a small window will first appear in which you will need to enter the code indicated at the top of it. According to the developer, this will serve as additional confirmation that you understand how to overclock the processor with this program and take upon yourself all the consequences of your actions.

The next window is already the main one for this program, and in it you will need to select the type of clock generator, which is determined by the motherboard model and is registered in the setfsb.txt file, which was studied above.

By selecting correct parameter Clock Generator, you will have access to changes in its parameters and, accordingly, you will be able to adjust the frequency of the FSB bus. The program will store the selected characteristics until the OS is rebooted. If you want to automate this operation, you will need to place a specially created one in startup. text editor bat file.
Another version of the program for overclocking an Intel processor is. Its functionality is almost similar to what we have already discussed SetFSB, for the better it differs only in the presence of a Russian interface. Therefore, it may well be suitable for beginner overclockers, as an introductory one.

The work is based on the same principle, that is, on interaction with the hardware of the motherboard. Supported boards in this utility are visible directly in the drop-down list, which is quite convenient. You need to select a manufacturer and then specify the type of PLL generator that is responsible for increasing the frequency of the system bus.
Once the necessary input parameters have been specified, you can begin to overclock the processor through the program.
AMD overclocking software
At one time, AMD, which had somewhat lost its position in the processor market, made a good marketing move. It released a series of FX processors with an unlocked multiplier and developed its own overclocking software. A program for overclocking an AMD processor is called AMD OverDrive and we will now get acquainted with it in more detail.
AMD OverDrive
So, the first thing you will see after launching this program for overclocking AMD processors will be the traditional warning from the manufacturers. In a nutshell, its content boils down to the fact that the operations performed to change processor parameters can lead to malfunctions in the operation of your computer, and by performing them, you are aware of your actions and accept responsibility. Of course, we have to agree with this. By clicking OK, the main program window will open with the main parameters of the processor installed in the system.

As you can see below, this information is similar to that obtained using the program CPU-Z and provides general, but comprehensive, information about the characteristics of a given processor.

The tools we are interested in in this program for overclocking AMD processors are located in the section on the left " Performance Control" In it you need to select the item “ Clock/Voltage"and begin to analyze the method of operation of the device.

In the figure presented above we see the processor performance before overclocking and, accordingly, the parameters available for adjustment. To access changing the value, you will need to enable the required function using the Turbo Core Control button, which will have a green highlight highlight before the operation.
In the window that opens, you need to check the box next to “ Enable Turbo Core».
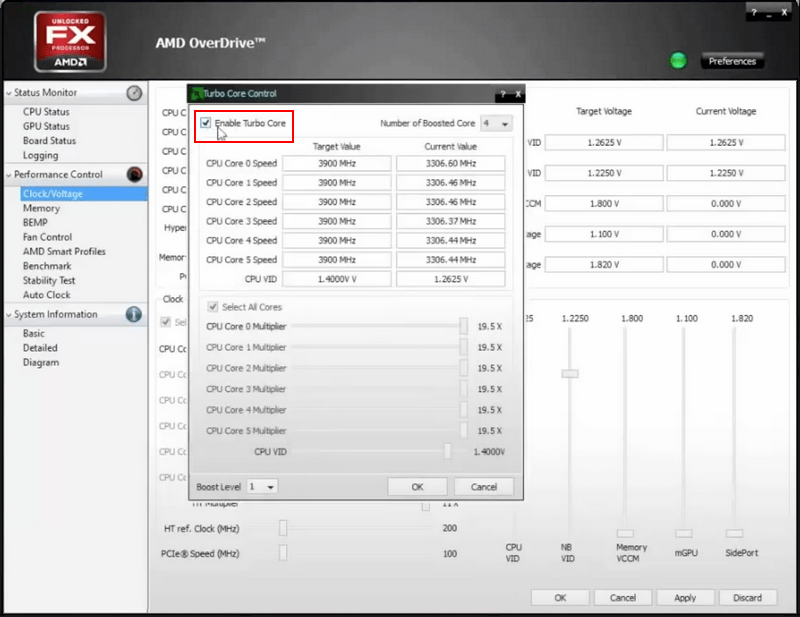
Thus, access to the processor parameters is obtained, and you can proceed directly to overclocking. The figure clearly shows that when you move the slider to the right in the “ Clock» the multiplier indicator increases by the available 3 points. A little higher you can see how the frequency indicators of the processor cores shift from the position of 3300 to 3900.

Test conducted using the utility CPU Speed Professional, shows the effective processor frequency with a default multiplier of 16.5.

The figure below shows the result of our manipulations. A CPU with a multiplier setting of 19.5 accelerates to 600 MHz.

The operation of the utility was examined in sufficient detail AMD OverDrive. I must say that this software from the manufacturer works perfectly with the entire line of processors and speeds up their work, starting with processors AMD Athlon.
Utilities for motherboards
Let's pay attention to another area of software development designed for overclocking. These are specialized utilities that are placed by some motherboard manufacturers on the included driver disk.
The three largest players in this market offer the following programs:

You can also look for analogues of such programs on the disks of lesser-known motherboard manufacturers, with the only exception that they usually come only with products in the upper price segment.
Software development direction
The most popular solutions for working with processors from leading manufacturers in this market were discussed above - Intel companies and AMD. It is worth noting that such a solution as a program for overclocking a processor directly from operating system, is dying out. Current trends in the development of basic systems that control the operation of hardware lead to this. Over the past ten years, there has been a significant expansion of BIOS functions and the transition of all motherboard manufacturers to using UEFI, its extended version.
Actually UEFI itself became an operating system in miniature. It has an attractive GUI, and mouse operation is supported. If earlier to edit parameters basic system I/O, the user required certain knowledge and skill in working with keyboard switching, but now there is no longer a need for this.
The conclusion from this is the following. Owners of AMD processors should not worry in the near future. The manufacturer itself has developed and supports a high-quality overclocking utility, and the latest models of devices in the series Ryzen are produced with good potential in this area. If you have an Intel processor, then in light of recent events in the motherboard industry, you should pay attention to studying UEFI. In the next few years, old motherboards will retire and overclocking the Intel platform can be done exclusively in this way. Even despite the release of the K series of processors with an unlocked multiplier, Intel gives preference to working with its brainchild - UEFI, and third-party developers in such conditions simply curtail their activities.
Conclusion
According to the established tradition among overclockers, let us remind you once again that all the consequences of switching the processor to an accelerated operating mode lie solely with the user, and no manufacturer is obliged to accept claims in case of unsuccessful actions. Don't forget this and always be careful. It is better to achieve a small but stable result than to rush and get nothing.
Video on the topic
Today we will talk about overclocking Intel processors and look in detail at the program with which it will be easiest to do this. But, in the beginning, we will find out what overclocking (from the English overclocking) of a processor is, why it is needed at all, and what consequences of overclocking await us in the future. People who overclock are called overlockers.
Conventionally, all overlockers are divided into three categories
- The first type is beginner and economical overlockers. In order to save cash they want maximum productivity while spending as little money as possible. In this case, the computer is assembled from not the most expensive components, which may be obviously outdated. In general, they buy what they have enough money for. Naturally, the performance is similar computer system far from the desired level. Therefore, owners of such equipment are starting to overclock the processor in order to at least slightly increase the performance of their PC.
- The second type includes the so-called experienced overlockers. Their goal is to get maximum performance and enjoyment from the overclocking process itself, without spending extra funds. Experienced overlockers, even at the stage of purchasing not the cheapest equipment, try to choose it with the expectation of a further upgrade. They thoughtfully choose every component of their future computer. If it is a motherboard, then it must have ample capabilities to support various components; if it is a processor, then it must have built-in overclocking capabilities, etc. As a result, very often similar systems after overclocking, they have at least comparable performance to top-end computers operating in nominal mode. But often such productivity is not vitally necessary, and the overlocker simply likes to enjoy a job well done.
- The third type of overclockers are extreme overclockers. For them, the goal of overclocking is to achieve the highest possible performance by any means necessary and regardless of price. They are in constant search older models, the most powerful components, reaching extremely low temperatures, etc. The main thing for them is to end up with a system with parameters that are inaccessible to most PC users.
Of course, such a division is conditional and there are no clear boundaries between overlockers. Over time, beginners move into the group of experienced ones; experienced ones, if they have the desire and opportunity, become extreme sports enthusiasts. But, one way or another, they all started somewhere, and any serious undertaking is preceded by theoretical preparation. So, first of all, we will deal with a little theory of processor overclocking.
Collecting system information
Before you start overclocking your processor, you need to have an idea of what you're dealing with. First you need to start studying your system. Identify all the components, study the motherboard manual, use information and diagnostic utilities, conduct performance tests, note the maximum and minimum temperatures under various system loads, etc. After overclocking the processor, you can compare the data obtained with the indicators that the system had before increasing the processor frequency. In addition, with the help of preliminary tests you can make sure that the system operates stably at the rated frequency and voltage.
Required programs
Both before and during overclocking, you will need special programs and utilities. Again, they are conventionally divided into several categories: programs for diagnostics, monitoring, overclocking, checking system stability, and utilities for measuring performance.
IN real life The clear boundaries between these categories are quite blurred. Using diagnostic programs, you can measure performance, and monitoring utilities can overclock the processor. It’s just that each program has a main direction for which it is optimally suited and several auxiliary non-core functions.
Diagnostic information software is designed primarily to determine the configuration of your system. The most powerful and functional of them are Lavalys Everest and SiSoftware Sandra.


But these packages are not limited solely to defining the system configuration. These software systems are capable of monitoring, measuring performance, and testing the stability of a computer. However, the use of such programs for all areas at once is not always justified, especially since they are distributed for a fee, and only a part of the capabilities are available in free packages. Such cumbersome programs can be replaced by less well-known ones, but this is no less effective utilities. For example, the CPU-Z utility is very popular among overlockers, capable of reporting information about both the processor itself and the motherboard and RAM. To carry out detailed control and manage memory timings, you can use the small MemSet program.
To overclock the processor, the best option is to use the BIOS. But, unfortunately, computer manufacturers do not always provide such an opportunity. In this case, you can use the universal SetFSB utility, which we will look at in more detail later. In addition, you should always familiarize yourself with the contents of the CD that comes with your motherboard. Manufacturers often supply their own programs with drivers, which have the ability to overclock the processor from Windows.
One important truth should always be remembered: none of the existing programs for overclocking processors cannot give you a 100% guarantee. But the chances will increase significantly if you use several different utilities for overclocking, monitoring and testing. The OCCT or S&M utilities will help you check the stability of the system.


Not a single hundred has been written to measure system performance. special programs. Such utilities test either the system as a whole or its components separately. An example of a simple but functional program is NovaBench.

CPU Overclocking Basics
Overclocking is the forced operation of the processor at frequencies higher than the nominal frequency. The reasons why overclocking is even feasible can be different. This reason could be a large safety margin built into the processor architecture by the manufacturer or some kind of marketing ploy. This is not so important, the main thing is to skillfully use the opportunities provided.
Despite the huge variety of computer components inside a PC, everything is largely standardized. This is caused by the need to synchronize components from different manufacturers. The starting point is the system bus frequency –FSB. At the same time, various buses on the motherboard (channels), which connect various components of the board, have an information transmission frequency lower than the FSB. Therefore, when setting their nominal frequencies, dividers are used. But since modern processors have a noticeably higher frequency, multipliers are used in order for it to operate at its nominal frequency.
Let's give an example. The Intel Core 2 Duo E6300 processor operates at a bus frequency of 266 MHz. Its multiplier is x7. The product of the FSB frequency by this multiplier will give the final processor frequency of 1.86 GHz. Therefore, in order to overclock the processor, it is necessary to either increase the FSB frequency or the multiplier.
Older models modern processors free factors are characteristic. But such processors have a high cost, which can be an order of magnitude higher than that of the younger processors of the family. Therefore, purchasing such processors is not entirely rational, since with the help of overclocking it is possible to achieve performance of younger processors comparable to the performance of their older brothers.
Therefore, overclocking any processor usually means increasing the FSB frequency. Taking acceleration as an example intel processor core 2 duo, then by increasing the bus frequency to 400 MHz, the processor frequency can increase to 2.8 GHz. If we increase the FSB to 500, then in this case the processor frequency will already be 3.5 GHz. This information is basic and already knowing it, you can head to the BIOS and start increasing the FSB frequency, thereby overclocking your processor. But still, before starting overclocking, you should carry out some preparatory work, which we will consider below.
Preparatory stage
Before you start overclocking the processor, you have to perform a couple of mandatory steps. The first step is to go to the website of your motherboard manufacturer and check if there is more information posted there. latest version BIOS. There are many cases where completely unsuccessful motherboards after BIOS updates found a second life, literally a second life. In addition, updating the version can not only correct the errors found, but also introduce new parameters and capabilities into the board’s BIOS. Find out which BIOS version you are using in present moment possible during the startup of the motherboard. If information appears for a very short period of time and you do not have time to read it, then press the Pause key on your keyboard. The BIOS version can also sometimes be seen using information and diagnostic utilities. Of course, not in all cases the new version BIOS is better It's more suitable for overclocking than the old one, but the new version at least fixes the errors of earlier versions.
Nuances of overclocking Intel Core processors
A characteristic feature of all processors with Core microarchitecture is high performance. Since they lend themselves well to overclocking, we will pay special attention to them.
Core processors except large quantity They also have a number of advantages that are unique to them, which still complicate the overclocking process. Such processors have their own feature - the so-called FSB Wall. This concept describes the maximum bus clock speed at which this processor can operate. By reducing the multiplier to x6, you can find out what maximum bus frequency your instance can operate at.
By the way, a processor with a nominal bus frequency of 200 MHz is almost never overclocked to a frequency exceeding 400 MHz FSB. This factor should be taken into account when choosing a Core series processor. Why pay for a processor from an older line, if it is much cheaper and easier to overclock a junior processor. It must be remembered that younger CPUs with a nominal x8 multiplier will most likely be limited due to the FSB Wall, and therefore the frequency after overclocking will not be able to go above 3.2 GHz. Therefore, in order not to limit yourself in advance to the maximum possible frequency, when purchasing, pay attention to processors that have a x9 multiplier.
Processors with a nominal bus frequency of 266 or 333 MHz are also selected as low-end ones and have a x7 multiplier. But here, in addition to the notorious FSB Wall, overclocking can be complicated in addition by the capabilities of the motherboard and RAM. Such processors should also be chosen with a multiplier of x8 or higher. However, here too a new danger awaits overlockers - FSB Strap.
FSB Strap, a parameter that characterizes not the processor itself, but the chipset and motherboard. This is the frequency at which the chipset switches operating modes. For example, after overclocking the processor, the performance of systems built on the motherboard Gigabyte board And Intel chipset P965 Express crashes immediately. But the motherboard is from manufacturer Asus, built on the same chipset, shows high performance even at 400 MHz. When testing the Asus Striker Extreme motherboard with the NVIDIA nForce 680i SLI chipset, performance dropped during the transition from FSB frequency 420 MHz to 425 MHz.
Overclocking the processor using the SetFSB program
Now that the theoretical part is over, we can start overclocking the Intel processor. As an example, let's take the very popular and effective SetFSB program.
After launching the utility, a similar window should appear on your screen.

At the very beginning you select a PLL chip. You can see which chip is installed either visually on the motherboard or using special utilities. It may happen that your chip is not on the list, then you will have to look for other utilities that support your chip type. As a last resort, you can contact the author of this utility and ask to add the chip you need to the program. But this procedure will take a lot of time and it is not a fact that the developer will even respond to your request.
After you have selected your chip, click the Get FSB button.

The window will display various frequency values, including the frequency at which the processor operates in at the moment. The current frequency is highlighted in the Current CPU Frequency window. In our case, this is a frequency of 1198.2 MHz.

We will overclock the processor by increasing the system bus frequency. To increase the named frequency, you need to move the slider located in the center of the window to the right. Tabs and sliders that are located nearby are best left as they are to avoid unexpected problems. If you want to increase the frequency adjustment range, check the box to the left of Ultra, as shown in the previous figure.
Now move the slider a little to the right. As a result, the frequency should increase by 10-15 MHz.

For the changes you have made to take effect, you must click the SetFSB button.

If after you clicked the SetFSB button, the computer freezes or turns off, do not be alarmed. This just means that you either specified the wrong PLL, or you overestimated the frequency very much. After a reboot, everything will return to normal and you can make changes. If you did everything correctly, the processor clock speed will increase. Look at the picture below.

In order to make sure that your computer is stable after overclocking, you will need to test it using a utility. We chose Preime95.

After launching the utility, click on the Just Stress Testing button, as shown in the figure above. Afterwards, a window like this should appear on your PC screen:

Select the third item and click OK. After this, testing your system should start.

If you wish, simultaneously with the Preime95 utility, you can run the HWMonitor utility, which will monitor the temperature of your processor, as well as other components during the test.

The Prime95 program has the ability to generate a serious load on the computer processor. Testing will be successful if the processor works stably for at least fifteen minutes and does not freeze. After successful completion of testing, you can try to further increase the processor frequency and run system testing again.
If you want to abort the test earlier, you can do this using the menu, as shown in the figure below.

By increasing the frequency and immediately checking the stability of the system using Prime95, you can achieve the maximum processor frequency at which it will work stably for a long period of time at maximum loads. After all the manipulations with overclocking and determining the optimal frequency, you need to add the SetFSB program to startup. Otherwise, all your changes will be lost after the first reboot of the PC.
First of all, create a bat script. Why do you need a regular one? standard Notepad, in which you need to make something like this:
c:\Program Files (x86)\SetFSB 2.2.129.95\setfsb.exe -w15 -s668 -cg
c:\Program Files (x86)\SetFSB 2.2.129.95\setfsb.exe is your path to the SetFSB utility on your computer. Naturally, it may differ for different users.
w15 – with this parameter you set the required delay before starting SetFSB. Time is indicated in seconds.
s668 – entry indicating the overclocking setting. This parameter is very important. In the figure, in our case, this is the number 668 (the first number to the right of the slider, which is located in the green field)

cg)